Endothelial function in obstructive sleep apnea
- PMID: 19249441
- PMCID: PMC4329644
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pcad.2008.08.002
Endothelial function in obstructive sleep apnea
Abstract
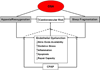
Untreated obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is an independent risk factor for hypertension, myocardial infarction, and stroke. The repetitive hypoxia/reoxygenation and sleep fragmentation associated with OSA impair endothelial function. Endothelial dysfunction, in turn, may mediate increased risk for cardiovascular diseases. Specifically, in OSA, endothelial nitric oxide availability and repair capacity are reduced, whereas oxidative stress and inflammation are enhanced. Treatment of OSA improves endothelial vasomotor tone and reduces inflammation. We review the evidence and possible mechanisms of endothelial dysfunction as well as the effect of treatment on endothelial function in OSA.
Figures
References
-
- Young T, Palta M, Dempsey J, et al. The occurrence of sleep disordered breathing among middle-aged adults. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:1230–1235. - PubMed
-
- Guilleminault C, Tilkian A, Dement WC. The sleep apnea syndromes. Annu Rev Med. 1976;27:465–484. - PubMed
-
- Peppard PE, Young T, Palta M, et al. Prospective study of the association between sleep-disordered breathing and hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1378–1384. - PubMed
-
- Peker Y, Kraiczi H, Hedner J, et al. An independent association between obstructive sleep apnea and coronary artery disease. Eur Respir J. 1999;13:179–184. - PubMed
-
- Yaggi HK, Concato J, Kernan WN, et al. Obstructive sleep apnea as a risk factor for stroke and death. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:2034–2041. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

