Dose effect of dual delivery of vascular endothelial growth factor and bone morphogenetic protein-2 on bone regeneration in a rat critical-size defect model
- PMID: 19249918
- PMCID: PMC2792218
- DOI: 10.1089/ten.tea.2008.0510
Dose effect of dual delivery of vascular endothelial growth factor and bone morphogenetic protein-2 on bone regeneration in a rat critical-size defect model
Abstract
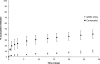
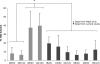
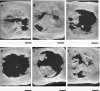
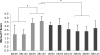
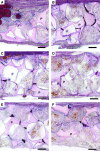
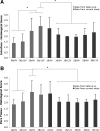
The dose effect of dual delivery of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) on bone regeneration was investigated in a rat cranial critical-size defect (CSD). It was hypothesized that decreasing amounts of BMP-2 would result in a dose-dependent decrease in bone formation, and that this reduction in bone formation could be reversed by adding increasing amounts of VEGF. In vitro release kinetics of VEGF or BMP-2 were examined over 28 days. Next, scaffolds were implanted within a rat cranial CSD containing different combinations of both BMP-2 and VEGF. At 12 weeks, samples were analyzed using microcomputed tomography and histology. In vitro, VEGF and BMP-2 exhibited burst release in the first 24 h followed by a significant decrease in release rate over 27 days. Overall, BMP-2 had a more sustained release versus VEGF. An in vivo dose-dependent decrease in percentage of bone fill (PBF) was observed for BMP-2. The addition of VEGF was unable to reverse this decrease in PBF, although improvements in the number of bridged defects did occur in some groups. This suggests that for this particular model simultaneous release of BMP-2 and VEGF does not increase bone formation over BMP-2 alone at 12 weeks.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dual delivery of an angiogenic and an osteogenic growth factor for bone regeneration in a critical size defect model.Bone. 2008 Nov;43(5):931-40. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2008.06.019. Epub 2008 Jul 14. Bone. 2008. PMID: 18675385 Free PMC article.
-
Dual release of growth factor from nanocomposite fibrous scaffold promotes vascularisation and bone regeneration in rat critical sized calvarial defect.Acta Biomater. 2018 Sep 15;78:36-47. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.07.050. Epub 2018 Jul 29. Acta Biomater. 2018. PMID: 30067947
-
Enhanced angiogenesis and osteogenesis in critical bone defects by the controlled release of BMP-2 and VEGF: implantation of electron beam melting-fabricated porous Ti6Al4V scaffolds incorporating growth factor-doped fibrin glue.Biomed Mater. 2015 Jun 24;10(3):035013. doi: 10.1088/1748-6041/10/3/035013. Biomed Mater. 2015. PMID: 26107105
-
Application of bone growth factors--the potential of different carrier systems.Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010 Mar;14(1):17-22. doi: 10.1007/s10006-009-0185-1. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010. PMID: 19865836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor for in vivo bone formation: A systematic review.J Orthop Translat. 2020 Jun 7;24:46-57. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2020.05.005. eCollection 2020 Sep. J Orthop Translat. 2020. PMID: 32642428 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of rhBMP-2 and VEGF in a vascularized bone allotransplant experimental model based on surgical neoangiogenesis.J Orthop Res. 2013 Apr;31(4):561-6. doi: 10.1002/jor.22277. Epub 2012 Nov 28. J Orthop Res. 2013. PMID: 23192572 Free PMC article.
-
Biomaterial delivery of morphogens to mimic the natural healing cascade in bone.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012 Sep;64(12):1257-76. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2012.05.006. Epub 2012 May 22. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012. PMID: 22626978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vascularized bone tissue engineering: approaches for potential improvement.Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2012 Oct;18(5):363-82. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEB.2012.0012. Epub 2012 Sep 4. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2012. PMID: 22765012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Screening of Hydroxyapatite Biomaterials for Alveolar Augmentation Using a Rat Calvaria Critical-Size Defect Model: Bone Formation/Maturation and Biomaterials Resolution.Biomolecules. 2022 Nov 12;12(11):1677. doi: 10.3390/biom12111677. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36421691 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin-specific hydrogels functionalized with VEGF for vascularization and bone regeneration of critical-size bone defects.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016 Apr;104(4):889-900. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.35626. Epub 2016 Jan 4. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016. PMID: 26662727 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Geiger M. Li R.H. Friess W. Collagen sponges for bone regeneration with rhBMP-2. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2003;55:1613. - PubMed
-
- Silva R.M. Elvira C. Mano J.F. San Roman J. Reis R.L. Influence of beta-radiation sterilisation in properties of new chitosan/soybean protein isolate membranes for guided bone regeneration. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2004;15:523. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi Y. Yamamoto M. Yamada K. Kawakami O. Tabata Y. Skull bone regeneration in nonhuman primates by controlled release of bone morphogenetic protein-2 from a biodegradable hydrogel. Tissue Eng. 2007;13:293. - PubMed
-
- Shea L.D. Wang D. Franceschi R.T. Mooney D.J. Engineered bone development from a pre-osteoblast cell line on three-dimensional scaffolds. Tissue Eng. 2000;6:605. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

