T-SPOT.TB responses during treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis
- PMID: 19250549
- PMCID: PMC2651889
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-9-23
T-SPOT.TB responses during treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis
Abstract
Background: Immune responses to Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens could serve as surrogate markers of treatment response.
Methods: Using the T-SPOT.TB assay and frozen peripheral blood mononuclear cells, we enumerated ESAT-6- and CFP-10-specific IFN-gamma-producing T cells over time in pulmonary TB patients receiving directly observed treatment. T cell responses (measured as "spot forming cells" or "SFCs") were assessed prior to treatment and at 16 and 24 weeks of treatment.
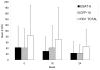
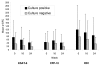
Results: 58 patients were evaluated, of whom 57 were HIV seronegative. Mean (SD) ESAT-6, CFP-10, and summed RD1 specific SFCs declined from 42.7 (72.7), 41.2 (66.4), and 83.8 (105.7) at baseline to 23.3 (39.4, p = 0.01), 23.2 (29.4, p = 0.18), and 46.5 (59.5, p = 0.02) at completion of 24 weeks of treatment, respectively. Only 10% of individuals with a baseline reactive test reverted to negative at treatment week 24. For the group that was culture positive at completion of 8 weeks of treatment compared to the culture negative group, the incidence rate ratio (IRR) of ESAT-6, CFP-10, and summed RD1 specific SFC counts were, respectively, 2.23 (p = 0.048), 1.51 (p = 0.20), and 1.83 (p = 0.047). Patients with cavitary disease had mean ESAT-6 specific SFC counts that were higher than those without cavitary disease (IRR 2.08, p = 0.034).
Conclusion: IFN-gamma-producing RD1-specific T cells, as measured in the T-SPOT.TB assay, may be directly related to bacterial load in patients undergoing treatment for pulmonary TB. However, high inter-subject variability in quantitative results coupled with failure of reversion to negative of qualitative results in most subjects at treatment completion may limit the utility of this assay as a surrogate marker for treatment efficacy.
Figures

References
-
- Pathan AA, Wilkinson KA, Klenerman P, McShane H, Davidson RN, Pasvol G, Hill AV, Lalvani A. Direct ex vivo analysis of antigen-specific IFN-gamma-secreting CD4 T cells in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected individuals: associations with clinical disease state and effect of treatment. J Immunol. 2001;167(9):5217–5225. - PubMed
-
- Lalvani A, Pathan AA, McShane H, Wilkinson RJ, Latif M, Conlon CP, Pasvol G, Hill AV. Rapid detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection by enumeration of antigen-specific T cells. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;163(4):824–828. - PubMed
-
- Goletti D, Carrara S, Vincenti D, Saltini C, Rizzi EB, Schinina V, Ippolito G, Amicosante M, Girardi E. Accuracy of an immune diagnostic assay based on RD1 selected epitopes for active tuberculosis in a clinical setting: a pilot study. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2006;12(6):544–550. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2006.01391.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

