miR-199a, a bone morphogenic protein 2-responsive MicroRNA, regulates chondrogenesis via direct targeting to Smad1
- PMID: 19251704
- PMCID: PMC2670138
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M807709200
miR-199a, a bone morphogenic protein 2-responsive MicroRNA, regulates chondrogenesis via direct targeting to Smad1
Abstract
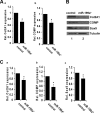
MicroRNAs (miRNA) are short non-coding RNA molecules that regulate a variety of biological processes. The role of miRNAs in BMP2-mediated biological processes is of considerable interest. A comparative miRNA array led to the isolation of several BMP2-responsive miRNAs. Among them, miR-199a(*) is of particular interest, because it was reported to be specifically expressed in the skeletal system. Here we demonstrate that miR-199a(*) is an early responsive target of BMP2: its level was dramatically reduced at 5 h, quickly increased at 24 h and remained higher thereafter in the course of BMP2-triggered chondrogenesis of a micromass culture of pluripotent C3H10T1/2 stem cells. miR-199a(*) significantly inhibited early chondrogenesis, as revealed by the reduced expression of early marker genes for chondrogenesis such as cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP), type II collagen, and Sox9, whereas anti-miR-199a(*) increased the expression of these chondrogenic marker genes. A computer-based prediction algorithm led to the identification of Smad1, a well established downstream molecule of BMP-2 signaling, as a putative target of miR-199a(*). The pattern of Smad1 mRNA expression exhibited the mirror opposite of miR-199a(*) expression following BMP-2 induction. Furthermore, miR-199a(*) demonstrated remarkable inhibition of both endogenous Smad1 as well as a reporter construct bearing the 3-untranslated region of Smad1 mRNA. In addition, mutation of miR-199a(*) binding sites in the 3'-untranslated region of Smad1 mRNA abolished miR-199a(*)-mediated repression of reporter gene activity. Mechanism studies revealed that miR-199a(*) inhibits Smad1/Smad4-mediated transactivation of target genes, and that overexpression of Smad1 completely corrects miR-199a(*)-mediated repression of early chondrogenesis. Taken together, miR-199a(*) is the first BMP2 responsive microRNA found to adversely regulate early chondrocyte differentiation via direct targeting of the Smad1 transcription factor.
Figures






References
-
- Lewis, B. P., Burge, C. B., and Bartel, D. P. (2005) Cell 120, 15-20 - PubMed
-
- Chan, S. P., and Slack, F. J. (2006) RNA Biol. 3, 97-100 - PubMed
-
- Chen, C. Z., Li, L., Lodish, H. F., and Bartel, D. P. (2004) Science 303, 83-86 - PubMed
-
- Esau, C., Kang, X., Peralta, E., Hanson, E., Marcusson, E. G., Ravichandran, L. V., Sun, Y., Koo, S., Perera, R. J., Jain, R., Dean, N. M., Freier, S. M., Bennett, C. F., Lollo, B., and Griffey, R. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279, 52361-52365 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

