Tetraspanins and vascular functions
- PMID: 19251723
- PMCID: PMC2695701
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvp080
Tetraspanins and vascular functions
Abstract
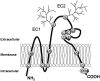
Tetraspanins are multiple membrane-spanning proteins that likely function as the organizers of membrane microdomains. Tetraspanins associate with other membrane-bound molecules such as cell-adhesion proteins, growth factor receptors, and Ig superfamily members and regulate key cellular processes such as adhesion, migration, and fusion. Tetraspanins are widely expressed in vascular and haematopoietic cells and are involved in both physiological and pathological processes related to angiogenesis, vascular injury, thrombosis, and haemostasis. A wide body of evidence suggests that tetraspanins directly regulate the development and functions of the vascular system and the pathogenesis of vascular diseases. This article reviews current understanding of the roles of tetraspanins in vascular functions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tetraspanins and intercellular interactions.Microcirculation. 2001 Jun;8(3):153-68. doi: 10.1038/sj/mn/7800076. Microcirculation. 2001. PMID: 11498779 Review.
-
The emerging role of tetraspanin microdomains on endothelial cells.Biochem Soc Trans. 2011 Dec;39(6):1667-73. doi: 10.1042/BST20110745. Biochem Soc Trans. 2011. PMID: 22103505 Review.
-
Vascular integrins: pleiotropic adhesion and signaling molecules in vascular homeostasis and angiogenesis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2003 Jun;60(6):1135-57. doi: 10.1007/s00018-003-2297-3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2003. PMID: 12861381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cadherins as modulators of angiogenesis and the structural integrity of blood vessels.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2000;19(1-2):1-5. doi: 10.1023/a:1026522216059. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2000. PMID: 11191048 Review.
-
Evaluating integrin function in models of angiogenesis and vascular permeability.Methods Enzymol. 2007;426:505-28. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(07)26021-5. Methods Enzymol. 2007. PMID: 17697897 Review.
Cited by
-
Tregs biomimetic nanoparticle to reprogram inflammatory and redox microenvironment in infarct tissue to treat myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury in mice.J Nanobiotechnology. 2022 Jun 3;20(1):251. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01445-2. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022. PMID: 35659239 Free PMC article.
-
Tetraspanins: integrating cell surface receptors to functional microdomains in homeostasis and disease.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2020 Aug;209(4):397-405. doi: 10.1007/s00430-020-00673-3. Epub 2020 Apr 9. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32274581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Migrasome and Tetraspanins in Vascular Homeostasis: Concept, Present, and Future.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jun 16;8:438. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00438. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32612990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling the Potential of Migrasomes: A Machine-Learning-Driven Signature for Diagnosing Acute Myocardial Infarction.Biomedicines. 2024 Jul 22;12(7):1626. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12071626. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39062199 Free PMC article.
-
A truncated form of CD9-partner 1 (CD9P-1), GS-168AT2, potently inhibits in vivo tumour-induced angiogenesis and tumour growth.Br J Cancer. 2011 Sep 27;105(7):1002-11. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2011.303. Epub 2011 Aug 23. Br J Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21863033 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hemler ME. Tetraspanin functions and associated microdomains. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:801–811. - PubMed
-
- Horejsi V, Vlcek C. Novel structurally distinct family of leucocyte surface glycoproteins including CD9, CD37, CD53 and CD63. FEBS Lett. 1991;288:1–4. - PubMed
-
- Maecker HT, Todd SC, Levy S. The tetraspanin superfamily: molecular facilitators. FASEB J. 1997;11:428–442. - PubMed
-
- Wright MD, Tomlinson MG. The ins and outs of the transmembrane 4 superfamily. Immunol Today. 1994;15:588–594. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

