DNA as an adhesin: Bacillus cereus requires extracellular DNA to form biofilms
- PMID: 19251901
- PMCID: PMC2681682
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01317-08
DNA as an adhesin: Bacillus cereus requires extracellular DNA to form biofilms
Abstract
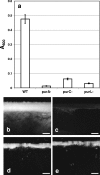
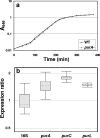
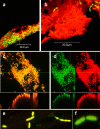
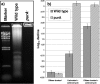
The soil saprophyte Bacillus cereus forms biofilms at solid-liquid interfaces. The composition of the extracellular polymeric matrix is not known, but biofilms of other bacteria are encased in polysaccharides, protein, and also extracellular DNA (eDNA). A Tn917 screen for strains impaired in biofilm formation at a solid-liquid interface yielded several mutants. Three mutants deficient in the purine biosynthesis genes purA, purC, and purL were biofilm impaired, but they grew planktonically like the wild type in Luria-Bertani broth. Biofilm populations had higher purA, purC, and purL transcript ratios than planktonic cultures, as measured by real-time PCR. Laser scanning confocal microscopy (LSCM) of BacLight-stained samples indicated that there were nucleic acids in the cell-associated matrix. This eDNA could be mobilized off the biofilm into an agarose gel matrix through electrophoresis, and it was a substrate for DNase. Glass surfaces exposed to exponentially growing populations acquired a DNA-containing conditioning film, as indicated by LSCM. Planktonic exponential-phase cells released DNA into an agarose gel matrix through electrophoresis, while stationary-phase populations did not do this. DNase treatment of planktonic exponential-phase populations rendered cells more susceptible than control populations to the DNA-interacting antibiotic actinomycin D. Exponential-phase purA cells did not contain detectable eDNA, nor did they convey a DNA-containing conditioning film to the glass surface. These results indicate that exponential-phase cells of B. cereus ATCC 14579 are decorated with eDNA and that biofilm formation requires DNA as part of the extracellular polymeric matrix.
Figures

References
-
- Allesen-Holm, M., K. B. Barken, L. Yang, M. Klausen, J. S. Webb, S. Kjelleberg, S. Molin, M. Givskov, and T. Tolker-Nielsen. 2006. A characterization of DNA release in Pseudomonas aeruginosa cultures and biofilms. Mol. Microbiol. 59:1114-1128. - PubMed
-
- Belem, M. A. F., B. F. Gibbs, and B. H. Lee. 1997. Enzymatic production of ribonucleotides from autolysates of Kluyveromyces marxianus grown on whey. J. Food Sci. 62:851-854+857.
-
- Böckelmann, U., A. Janke, R. Kuhn, T. R. Neu, J. Wecke, J. R. Lawrence, and U. Szewzyk. 2006. Bacterial extracellular DNA forming a defined network-like structure. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 262:31-38. - PubMed
-
- Bone, E. J., and D. J. Ellar. 1989. Transformation of Bacillus thuringiensis by electroporation. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 49:171-177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

