Immunosuppressive treatment for aplastic anemia: are we hitting the ceiling?
- PMID: 19252172
- PMCID: PMC2649354
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2008.002329
Immunosuppressive treatment for aplastic anemia: are we hitting the ceiling?
Abstract
The combination of antithymocyte globulin of horse origin and cyclosporine A is the standard treatment for aplastic anemia in patients not eligible for bone marrow transplantation. In this perspective article, Drs. Passweg and Tichelli discuss the current immunosuppressive therapy of aplastic anemia. See related article on page 348.
Figures
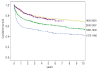
Comment on
-
Treatment of severe aplastic anemia with a combination of horse antithymocyte globulin and cyclosporine, with or without sirolimus: a prospective randomized study.Haematologica. 2009 Mar;94(3):348-54. doi: 10.3324/haematol.13829. Epub 2009 Jan 30. Haematologica. 2009. PMID: 19181786 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Camitta BM, Rappeport JM, Parkman R, Nathan DG. Selection of patients for bone marrow transplantation in severe aplastic anemia. Blood. 1975;45:355–63. - PubMed
-
- Bacigalupo A, Brand R, Oneto R, Bruno B, Socie G, Passweg J, et al. Treatment of acquired severe aplastic anemia: bone marrow transplantation compared with immunosuppressive therapy - the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation experience. Semin Hematol. 2000;37:69–80. - PubMed
-
- Socie G, Rosenfeld S, Frickhofen N, Gluckman E, Tichelli A. Late clonal diseases of treated aplastic anemia. Semin Hematol. 2000;37:91–101. - PubMed
-
- Kojima S, Ohara A, Tsuchida M, Kudoh T, Hanada R, Okimoto Y, et al. Risk factors for evolution of acquired aplastic anemia into myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia after immunosuppressive therapy in children. Blood. 2002;100:786–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

