The Axl receptor tyrosine kinase confers an adverse prognostic influence in pancreatic cancer and represents a new therapeutic target
- PMID: 19252414
- PMCID: PMC2678175
- DOI: 10.4161/cbt.8.7.7923
The Axl receptor tyrosine kinase confers an adverse prognostic influence in pancreatic cancer and represents a new therapeutic target
Abstract
Background: Pancreatic cancer is a near uniformly lethal disease and a better understanding of the molecular basis of this malignancy may lead to improved therapeutics. The Axl receptor tyrosine kinase is implicated in cellular transformation and tumor progression, although its role in pancreatic cancer has not been previously documented.
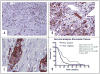
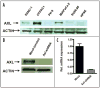
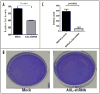
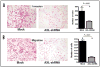
Results: Axl labeling was present in 54 of 99 (55%), and was absent in 45 of 99 (45%) cases, respectively. Axl expression in pancreatic cancer was significantly associated with lymph node metastases (p < 0.01), and a shorter median survival (12 versus 18 months, p < 0.01), than in tumors with negative labeling. Stable knockdown of Axl resulted in significant reduction in cell viability (p < 0.001), anchorage independent growth (p = 0.0031), as well as attenuation of migratory (p < 0.001) and invasive properties (p < 0.005), compared to vector-transfected cells. Profound inhibition of p42/p44 MAP kinase and PI-3kinase/Akt effector pathways was observed in MIAPaCa-2 cells with loss of Axl function. The reduction in invasion and migration upon Axl knockdown was mirrored by a decrease in the amounts of activated (GTP-bound) GTPase proteins Rho and Rac, significant downregulation in transcript levels of the epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT)-associated transcription factors slug, snail and twist, and significant decrease in matrix metalloproteinase MMP-9 mRNA levels.
Materials: The immunohistochemical expression of Axl protein was assessed in a panel of 99 archival pancreatic cancers. Endogenous Axl expression was stably downregulated by lentiviral short hairpin shRNA directed against AXL mRNA in MIAPaCa-2 cells, and the effects on cell viability, anchorage independent growth, invasion, migration and intracellular effector pathways was assessed, by comparing to lentiviral vector-transfected cells.
Conclusion: Expression of Axl tyrosine kinase in pancreatic cancers confers an adverse prognostic influence, and represents a new therapeutic target in this malignancy.
Figures

References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Murray T, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2008;58:71–96. - PubMed
-
- O’Reilly EM, Abou-Alfa GK. Cytotoxic therapy for advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Seminars in oncology. 2007;34:347–53. - PubMed
-
- Strimpakos A, Saif MW, Syrigos KN. Pancreatic cancer: from molecular pathogenesis to targeted therapy. Cancer metastasis reviews. 2008;27:495–522. - PubMed
-
- Bennasroune A, Gardin A, Aunis D, Cremel G, Hubert P. Tyrosine kinase receptors as attractive targets of cancer therapy. Critical reviews in oncology/hematology. 2004;50:23–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
