RNase L downmodulation of the RNA-binding protein, HuR, and cellular growth
- PMID: 19252527
- PMCID: PMC3071643
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2009.16
RNase L downmodulation of the RNA-binding protein, HuR, and cellular growth
Abstract
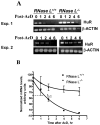
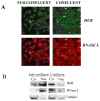
Ribonuclease L (RNase L) is an intracellular enzyme that is vital in innate immunity, but also is a tumor suppressor candidate. Here, we show that overexpression of RNase L decreases cellular growth and downmodulates the RNA-binding protein, HuR, a regulator of cell-cycle progression and tumorigenesis. The effect is temporal, occurring in specific cell-cycle phases and correlated with the cytoplasmic localization of RNase L. Both cellular growth and HuR were increased in RNASEL-null mouse fibroblast lines when compared to wild-type cells. Moreover, the stability of HuR mRNA was enhanced in RNASEL-null cells. The HuR 3' untranslated region (UTR), which harbors U-rich and adenylate-uridylate-rich elements, was potently responsive to RNase L when compared to control 3' UTR. Our results may offer a new explanation to the tumor suppressor function of RNase L.
Figures




References
-
- Silverman RH. Implications for RNase L in prostate cancer biology. Biochemistry. 2003;42:1805–12. - PubMed
-
- Carpten J, et al. Germline mutations in the ribonuclease L gene in families showing linkage with HPC1. Nat Genet. 2002;30:181–4. - PubMed
-
- Zhou A, et al. Impact of RNase L overexpression on viral and cellular growth and death. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 1998;18:953–61. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

