Feeding a ROS-generator to Caenorhabditis elegans leads to increased expression of small heat shock protein HSP-16.2 and hormesis
- PMID: 19252938
- PMCID: PMC2654055
- DOI: 10.1007/s12263-009-0113-x
Feeding a ROS-generator to Caenorhabditis elegans leads to increased expression of small heat shock protein HSP-16.2 and hormesis
Abstract
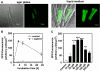
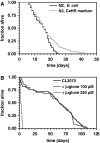
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are thought to be a driving force in the aging process. In transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP) under control of the hsp-16.2 promoter (CL2070) 100 muM of the ROS-generator juglone induced GFP-expression. This was associated with translocation of DAF-16 to the nucleus as visualized in a transgenic strain expressing a DAF-16::GFP fusion protein (TJ356) and with increased cellular levels of reduced glutathione. RNA-interference for DAF-16 in CL2070 blocked the juglone-induced HSP-16.2 expression and the increase in glutathione levels. Higher concentrations of juglone did not further increase the adaptive responses but caused premature death, indicating hormetic adaptations unless the stressor exceeds the intrinsic protective capacity. The addition of the ROS-scavenger ascorbic acid finally blocked lifespan reductions and all of the adaptations to juglone stressing that ROS are indeed the molecular species that require protective response.
Figures

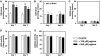

Similar articles
-
Caenorhabditis elegans lifespan extension caused by treatment with an orally active ROS-generator is dependent on DAF-16 and SIR-2.1.Biogerontology. 2010 Apr;11(2):183-95. doi: 10.1007/s10522-009-9239-x. Epub 2009 Jul 14. Biogerontology. 2010. PMID: 19597959
-
Phytochemicals-induced hormesis protects Caenorhabditis elegans against α-synuclein protein aggregation and stress through modulating HSF-1 and SKN-1/Nrf2 signaling pathways.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Jun;102:812-822. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.128. Epub 2018 Apr 5. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29605769
-
Epigallocatechin gallate inhibits beta amyloid oligomerization in Caenorhabditis elegans and affects the daf-2/insulin-like signaling pathway.Phytomedicine. 2010 Sep;17(11):902-9. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2010.03.008. Epub 2010 Apr 9. Phytomedicine. 2010. PMID: 20382008
-
Selenite protects Caenorhabditis elegans from oxidative stress via DAF-16 and TRXR-1.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2014 Apr;58(4):863-74. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201300404. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2014. PMID: 24254253
-
Realgar bioleaching solution suppress ras excessive activation by increasing ROS in Caenorhabditis elegans.Arch Pharm Res. 2014 Mar;37(3):390-8. doi: 10.1007/s12272-013-0182-7. Epub 2013 Jun 19. Arch Pharm Res. 2014. PMID: 23775476
Cited by
-
Shaping longevity early in life: developmental ROS and H3K4me3 set the clock.Cell Cycle. 2021 Nov;20(22):2337-2347. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2021.1986317. Epub 2021 Oct 17. Cell Cycle. 2021. PMID: 34657571 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression, metabolic regulation and stress tolerance during diapause.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010 Jul;67(14):2405-24. doi: 10.1007/s00018-010-0311-0. Epub 2010 Mar 7. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010. PMID: 20213274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Feedback regulation via AMPK and HIF-1 mediates ROS-dependent longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Oct 21;111(42):E4458-67. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1411199111. Epub 2014 Oct 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25288734 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro and In Vivo Insights into a Broccoli Byproduct as a Healthy Ingredient for the Management of Alzheimer's Disease and Aging through Redox Biology.J Agric Food Chem. 2024 Mar 13;72(10):5197-5211. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c05609. Epub 2024 Mar 5. J Agric Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 38477041 Free PMC article.
-
The neurohormone tyramine stimulates the secretion of an insulin-like peptide from the Caenorhabditis elegans intestine to modulate the systemic stress response.PLoS Biol. 2025 Jan 28;23(1):e3002997. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002997. eCollection 2025 Jan. PLoS Biol. 2025. PMID: 39874242 Free PMC article.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05016-3', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/s0076-6879(84)05016-3'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '6727660', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6727660/'}]}
- Aebi H (1986) Catalase in vitro. Meth Enzymol 105:121–126 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1242/jeb.00433', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.00433'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC3951750', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3951750/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12796460', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12796460/'}]}
- Avery L, Shtonda BB (2003) Food transport in the C. elegans pharynx. J Exp Biol 206:2441–2457 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC1213120', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1213120/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '4366476', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/4366476/'}]}
- Brenner S (1974) The genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 77:71–94 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/0003-9861(83)90499-X', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(83)90499-x'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '6687666', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6687666/'}]}
- Blum J, Fridovich I (1983) Superoxide, hydrogen peroxide, and oxygen toxicity in two free-living nematode species. Arch Biochem Biophys 222:35–43 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1155/JBB/2006/45716', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1155/jbb/2006/45716'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC1559919', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1559919/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '17057364', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17057364/'}]}
- Clark J, Ding S (2006) Generation of RNAi libraries for high-throughput screens. J Biomed Biotechnol 2006:1–7 - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
