Cytoplasmic polyadenylation and cytoplasmic polyadenylation element-dependent mRNA regulation are involved in Xenopus retinal axon development
- PMID: 19254368
- PMCID: PMC2661069
- DOI: 10.1186/1749-8104-4-8
Cytoplasmic polyadenylation and cytoplasmic polyadenylation element-dependent mRNA regulation are involved in Xenopus retinal axon development
Abstract
Background: Translation in axons is required for growth cone chemotropic responses to many guidance cues. Although locally synthesized proteins are beginning to be identified, how specific mRNAs are selected for translation remains unclear. Control of poly(A) tail length by cytoplasmic polyadenylation element (CPE) binding protein 1 (CPEB1) is a conserved mechanism for mRNA-specific translational regulation that could be involved in regulating translation in axons.
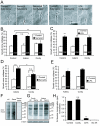
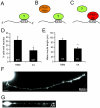
Results: We show that cytoplasmic polyadenylation is required in Xenopus retinal ganglion cell (RGC) growth cones for translation-dependent, but not translation-independent, chemotropic responses in vitro, and that inhibition of CPE binding through dominant-negative interference severely reduces axon outgrowth in vivo. CPEB1 mRNA transcripts are present at low levels in RGCs but, surprisingly, CPEB1 protein was not detected in eye or brain tissue, and CPEB1 loss-of-function does not affect chemotropic responses or pathfinding in vivo. UV cross-linking experiments suggest that CPE-binding proteins other than CPEB1 in the retina regulate retinal axon development.
Conclusion: These results indicate that cytoplasmic polyadenylation and CPE-mediated translational regulation are involved in retinal axon development, but that CPEB1 may not be the key regulator of polyadenylation in the developing retina.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Meiosis requires a translational positive loop where CPEB1 ensues its replacement by CPEB4.EMBO J. 2010 Jul 7;29(13):2182-93. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2010.111. Epub 2010 Jun 8. EMBO J. 2010. PMID: 20531391 Free PMC article.
-
The poly(rC)-binding protein alphaCP2 is a noncanonical factor in X. laevis cytoplasmic polyadenylation.RNA. 2011 May;17(5):944-56. doi: 10.1261/rna.2587411. Epub 2011 Mar 28. RNA. 2011. PMID: 21444632 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoplasmic polyadenylation-element-binding protein (CPEB)1 and 2 bind to the HIF-1alpha mRNA 3'-UTR and modulate HIF-1alpha protein expression.Biochem J. 2009 Jan 1;417(1):235-46. doi: 10.1042/BJ20081353. Biochem J. 2009. PMID: 18752464
-
Cytoplasmic mRNA polyadenylation and translation assays.Methods Mol Biol. 2006;322:183-98. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-000-3_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16739724 Review.
-
Cytoplasmic Polyadenylation Element Binding Protein 1 and Atherosclerosis: Prospective Target and New Insights.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2024;22(2):95-105. doi: 10.2174/0115701611258090231221082502. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38284693 Review.
Cited by
-
Loss of CPEB3 Upregulates MEGF10 to Impair Mosaic Development of ON Starburst Amacrine Cells.Front Mol Neurosci. 2016 Oct 24;9:105. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2016.00105. eCollection 2016. Front Mol Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27822178 Free PMC article.
-
Translational activation of maternally derived mRNAs in oocytes and early embryos and the role of embryonic poly(A) binding protein (EPAB).Biol Reprod. 2019 May 1;100(5):1147-1157. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioz034. Biol Reprod. 2019. PMID: 30806655 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coupling of NF-protocadherin signaling to axon guidance by cue-induced translation.Nat Neurosci. 2013 Feb;16(2):166-73. doi: 10.1038/nn.3290. Epub 2013 Jan 6. Nat Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23292679 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-binding proteins and translational regulation in axons and growth cones.Front Neurosci. 2013 May 23;7:81. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2013.00081. eCollection 2013. Front Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23734093 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the roles of local translation from the axonal transcriptome.Open Biol. 2012 Jun;2(6):120079. doi: 10.1098/rsob.120079. Open Biol. 2012. PMID: 22773949 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

