Functional claudication distance: a reliable and valid measurement to assess functional limitation in patients with intermittent claudication
- PMID: 19254382
- PMCID: PMC2667172
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2261-9-9
Functional claudication distance: a reliable and valid measurement to assess functional limitation in patients with intermittent claudication
Abstract
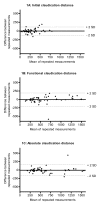
Background: Disease severity and functional impairment in patients with intermittent claudication is usually quantified by the measurement of pain-free walking distance (intermittent claudication distance, ICD) and maximal walking distance (absolute claudication distance, ACD). However, the distance at which a patient would prefer to stop because of claudication pain seems a definition that is more correspondent with the actual daily life walking distance. We conducted a study in which the distance a patient prefers to stop was defined as the functional claudication distance (FCD), and estimated the reliability and validity of this measurement.
Methods: In this clinical validity study we included patients with intermittent claudication, following a supervised exercise therapy program. The first study part consisted of two standardised treadmill tests. During each test ICD, FCD and ACD were determined. Primary endpoint was the reliability as represented by the calculated intra-class correlation coefficients. In the second study part patients performed a standardised treadmill test and filled out the Rand-36 questionnaire. Spearman's rho was calculated to assess validity.
Results: The intra-class correlation coefficients of ICD, FCD and ACD were 0.940, 0.959, and 0.975 respectively. FCD correlated significantly with five out of nine domains, namely physical function (rho = 0.571), physical role (rho = 0.532), vitality (rho = 0.416), pain (rho = 0.416) and health change (rho = 0.414).
Conclusion: FCD is a reliable and valid measurement for determining functional capacity in trained patients with intermittent claudication. Furthermore it seems that FCD better reflects the actual functional impairment. In future studies, FCD could be used alongside ICD and ACD.
Figures
References
-
- Jongert MWA, Hendriks HJM, Van Hoek J, Klaasboer-Kogelman K, Robeer GG, Simens B, Voort S van der, Smit B. KNGF-richtlijn Claudicatio Intermittens. Nederlands Tijdschrift voor Fysiotherapie. 2003. pp. 3–58.
-
- Gardner AW, Katzel LI, Sorkin JD, Bradham DD, Hochberg MC, Flinn WR, Goldberg AP. Exercise rehabilitation improves functional outcomes and peripheral circulation in patients with intermittent claudication: a randomized controlled trial. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2001;49:755–762. doi: 10.1046/j.1532-5415.2001.49152.x. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources