Characterization of engineered channelrhodopsin variants with improved properties and kinetics
- PMID: 19254539
- PMCID: PMC2717302
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2008.11.034
Characterization of engineered channelrhodopsin variants with improved properties and kinetics
Abstract
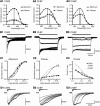
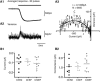
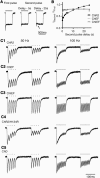
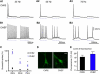
Channelrhodopsin 2 (ChR2), a light-activated nonselective cationic channel from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, has become a useful tool to excite neurons into which it is transfected. The other ChR from Chlamydomonas, ChR1, has attracted less attention because of its proton-selective permeability. By making chimeras of the transmembrane domains of ChR1 and ChR2, combined with site-directed mutagenesis, we developed a ChR variant, named ChEF, that exhibits significantly less inactivation during persistent light stimulation. ChEF undergoes only 33% inactivation, compared with 77% for ChR2. Point mutation of Ile(170) of ChEF to Val (yielding "ChIEF") accelerates the rate of channel closure while retaining reduced inactivation, leading to more consistent responses when stimulated above 25 Hz in both HEK293 cells and cultured hippocampal neurons. In addition, these variants have altered spectral responses, light sensitivity, and channel selectivity. ChEF and ChIEF allow more precise temporal control of depolarization, and can induce action potential trains that more closely resemble natural spiking patterns.
Figures


References
-
- Nagel G., Ollig D., Fuhrmann M., Kateriya S., Musti A.M. Channelrhodopsin-1: a light-gated proton channel in green algae. Science. 2002;296:2395–2398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

