Adipocyte CREB promotes insulin resistance in obesity
- PMID: 19254572
- PMCID: PMC2730923
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2009.01.006
Adipocyte CREB promotes insulin resistance in obesity
Abstract
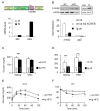
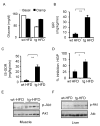
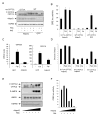
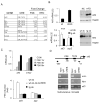
Increases in adiposity trigger metabolic and inflammatory changes that interfere with insulin action in peripheral tissues, culminating in beta cell failure and overt diabetes. We found that the cAMP Response Element Binding protein (CREB) is activated in adipose cells under obese conditions, where it promotes insulin resistance by triggering expression of the transcriptional repressor ATF3 and thereby downregulating expression of the adipokine hormone adiponectin as well as the insulin-sensitive glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4). Transgenic mice expressing a dominant-negative CREB transgene in adipocytes displayed increased whole-body insulin sensitivity in the contexts of diet-induced and genetic obesity, and they were protected from the development of hepatic steatosis and adipose tissue inflammation. These results indicate that adipocyte CREB provides an early signal in the progression to type 2 diabetes.
Figures

References
-
- Berg AH, Combs TP, Du X, Brownlee M, Scherer PE. The adipocyte-secreted protein Acrp30 enhances hepatic insulin action. Nat Med. 2001;7:947–953. - PubMed
-
- Berger J, Biswas C, Vicario PP, Strout HV, Saperstein R, Pilch PF. Decreased expression of the insulin-responsive glucose transporter in diabetes and fasting. Nature. 1989;340:70–72. - PubMed
-
- Blendy J, Kaestner K, Weinbauer G, Nieschlag E, Schutz G. Severe impairment of spermatogenesis in mice lacking the CREM gene. Nature. 1996;380:162–165. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

