Independent beta-arrestin2 and Gq/protein kinase Czeta pathways for ERK stimulated by angiotensin type 1A receptors in vascular smooth muscle cells converge on transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor
- PMID: 19254952
- PMCID: PMC2673264
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M808176200
Independent beta-arrestin2 and Gq/protein kinase Czeta pathways for ERK stimulated by angiotensin type 1A receptors in vascular smooth muscle cells converge on transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor
Abstract
Recent studies in receptor-transfected cell lines have demonstrated that extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) activation by angiotensin type 1A receptor and other G protein-coupled receptors can be mediated by both G protein-dependent and beta-arrestin-dependent mechanisms. However, few studies have explored these mechanisms in primary cultured cells expressing endogenous levels of receptors. Accordingly, here we utilized the beta-arrestin biased agonist for the angiotensin type 1A receptor, SII-angiotensin (SII), and RNA interference techniques to investigate angiotensin II (ANG)-activated beta-arrestin-mediated mitogenic signaling pathways in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Both ANG and SII induced DNA synthesis via the ERK activation cascade. Even though SII cannot induce calcium influx (G protein activation) after receptor stimulation, it does cause ERK activation, although less robustly than ANG. Activation by both ligands is diminished by depletion of beta-arrestin2 by small interfering RNA, although the effect is more complete with SII. ERK activation at early time points but not later time points is strongly inhibited by those protein kinase C inhibitors that can block protein kinase Czeta. Moreover, ANG- and SII-mediated ERK activation require transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor via metalloprotease 2/9 and Src kinase. beta-Arrestin2 facilitates ANG and SII stimulation of Src-mediated phosphorylation of Tyr-845 on the EGFR, a known site for Src phosphorylation. These studies delineate a convergent mechanism by which G protein-dependent and beta-arrestin-dependent pathways can independently mediate ERK-dependent transactivation of the EGFR in vascular smooth muscle cells thus controlling cellular proliferative responses.
Figures
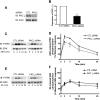
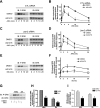
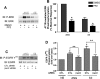
References
-
- Drake, M. T., Shenoy, S. K., and Lefkowitz, R. J. (2006) Circ. Res. 99 570–582 - PubMed
-
- DeWire, S. M., Ahn, S., Lefkowitz, R. J., and Shenoy, S. K. (2007) Annu. Rev. Physiol. 69 483–510 - PubMed
-
- Demoliou-Mason, C. D. (1998) Biol. Signals Recept. 7 90–97 - PubMed
-
- Nozawa, Y., Matsuura, N., Miyake, H., Yamada, S., and Kimura, R. (1999) Life Sci. 64 2061–2070 - PubMed
-
- Wassmann, S., and Nickenig, G. (2006) J. Hypertens. 24 S15–S21 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

