The chromatin remodeling factor CHD8 interacts with elongating RNA polymerase II and controls expression of the cyclin E2 gene
- PMID: 19255092
- PMCID: PMC2677868
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp101
The chromatin remodeling factor CHD8 interacts with elongating RNA polymerase II and controls expression of the cyclin E2 gene
Abstract
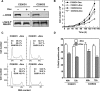
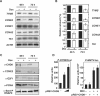
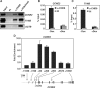
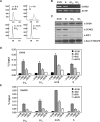
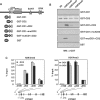
CHD8 is a chromatin remodeling ATPase of the SNF2 family. We found that depletion of CHD8 impairs cell proliferation. In order to identify CHD8 target genes, we performed a transcriptomic analysis of CHD8-depleted cells, finding out that CHD8 controls the expression of cyclin E2 (CCNE2) and thymidylate synthetase (TYMS), two genes expressed in the G1/S transition of the cell cycle. CHD8 was also able to co-activate the CCNE2 promoter in transient transfection experiments. Chromatin immunoprecipitation experiments demonstrated that CHD8 binds directly to the 5' region of both CCNE2 and TYMS genes. Interestingly, both RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) and CHD8 bind constitutively to the 5' promoter-proximal region of CCNE2, regardless of the cell-cycle phase and, therefore, of the expression of CCNE2. The tandem chromodomains of CHD8 bind in vitro specifically to histone H3 di-methylated at lysine 4. However, CHD8 depletion does not affect the methylation levels of this residue. We also show that CHD8 associates with the elongating form of RNAPII, which is phosphorylated in its carboxy-terminal domain (CTD). Furthermore, CHD8-depleted cells are hypersensitive to drugs that inhibit RNAPII phosphorylation at serine 2, suggesting that CHD8 is required for an early step of the RNAPII transcription cycle.
Figures
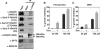
References
-
- Saunders A, Core LJ, Lis JT. Breaking barriers to transcription elongation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006;7:557–567. - PubMed
-
- Li B, Carey M, Workman JL. The role of chromatin during transcription. Cell. 2007;128:707–719. - PubMed
-
- Smith CL, Peterson CL. ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2005;65:115–148. - PubMed
-
- Flaus A, Owen-Hughes T. Mechanisms for ATP-dependent chromatin remodelling: farewell to the tuna-can octamer? Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2004;14:165–173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

