Nuclear ferritin: a ferritoid-ferritin complex in corneal epithelial cells
- PMID: 19255152
- PMCID: PMC4793724
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.08-3170
Nuclear ferritin: a ferritoid-ferritin complex in corneal epithelial cells
Abstract
Purpose: Ferritin is an iron storage protein that is generally cytoplasmic. However, in embryonic avian corneal epithelial (CE) cells, the authors previously observed that the ferritin was predominantly nuclear. They also obtained evidence that this ferritin protects DNA from oxidative damage by UV light and hydrogen peroxide and that the nuclear localization involves a tissue-specific nuclear transporter, termed ferritoid. In the present investigation, the authors have determined additional properties of the nuclear ferritoid-ferritin complexes.
Methods: For biochemical characterization, a combination of molecular sieve chromatography, immunoblotting, and nuclear-cytoplasmic fractionation was used; DNA binding was analyzed by electrophoretic mobility shift assay.
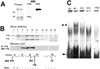
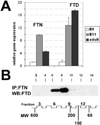
Results: The CE nuclear ferritin complex has characteristics that differentiate it from a "typical" cytoplasmic ferritin, including the presence of ferritin and ferritoid subunits; a molecular weight of approximately 260 kDa, which is approximately half that of cytoplasmic ferritin; its iron content, which is below our limits of detection; and its ability to bind to DNA.
Conclusions: Within CE cell nuclei, ferritin and ferritoid are coassembled into stable complex(es) present in embryonic and adult corneas. Thus, ferritoid not only serves transiently as a nuclear transporter for ferritin, it remains as a component of a unique ferritoid-ferritin nuclear complex.
Figures


References
-
- Stohs SJ, Bagchi D. Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of metal ions. Free Radical Biol Med. 1995;18:321–336. - PubMed
-
- Henle ES, Luo Y, Gassmann W, Linn S. Oxidative damage to DNA constituents by iron-mediated Fenton reactions: the deoxyguanosine family. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:21177–21186. - PubMed
-
- Luo Y, Henle ES, Linn S. Oxidative damage to DNA constituents by iron-mediated Fenton reactions: the deoxycytidine family. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:21167–21176. - PubMed
-
- Shimmura S, Suematsu M, Shimoyama M, Tsubota K, Oguchi Y, Ishimura Y. Subthreshold UV radiation-induced peroxide formation in cultured corneal epithelial cells: the protective effects of lactoferrin. Exp Eye Res. 1996;63:519–526. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

