The absence of Hck, Fgr, and Lyn tyrosine kinases augments lung innate immune responses to Pneumocystis murina
- PMID: 19255189
- PMCID: PMC2681740
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01441-08
The absence of Hck, Fgr, and Lyn tyrosine kinases augments lung innate immune responses to Pneumocystis murina
Abstract
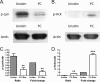
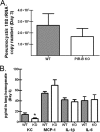
Src family tyrosine kinases (SFKs) phosphorylate immunotyrosine activation motifs in the cytoplasmic tail of multiple immunoreceptors, leading to the initiation of cellular effector functions, such as phagocytosis, reactive oxygen species production, and cytokine production. SFKs also play important roles in regulating these responses through the activation of immunotyrosine inhibitory motif-containing inhibitory receptors. As myeloid cells preferentially express the SFKs Hck, Fgr, and Lyn, we questioned the role of these kinases in innate immune responses to Pneumocystis murina. Increased phosphorylation of Hck was readily detectable in alveolar macrophages after stimulation with P. murina. We further observed decreased phosphorylation of Lyn on its C-terminal inhibitory tyrosine in P. murina-stimulated alveolar macrophages, indicating that SFKs were activated in alveolar macrophages in response to P. murina. Mice deficient in Hck, Fgr, and Lyn exhibited augmented clearance 3 and 7 days after intratracheal administration of P. murina, which correlated with elevated levels of interleukin 1beta (IL-1beta), IL-6, CXCL1/KC, CCL2/monocyte chemoattractant protein 1, and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in lung homogenates and a dramatic increase in macrophage and neutrophil recruitment. Augmented P. murina clearance was also observed in Lyn(-/-) mice 3 days postchallenge, although the level was less than that observed in Hck(-/-) Fgr(-/-) Lyn(-/-) mice. A correlate to augmented clearance of P. murina in Hck(-/-) Fgr(-/-) Lyn(-/-) mice was a greater ability of alveolar macrophages from these mice to kill P. murina in vitro, suggesting that SFKs regulate the alveolar macrophage effector function against P. murina. Mice deficient in paired immunoglobulin receptor B (PIR-B), an inhibitory receptor activated by SFKs, did not exhibit enhanced inflammatory responsiveness to or clearance of P. murina. Our results suggest that SFKs regulate innate lung responses to P. murina in a PIR-B-independent manner.
Figures




Similar articles
-
IL-33 and M2a alveolar macrophages promote lung defense against the atypical fungal pathogen Pneumocystis murina.J Immunol. 2011 Feb 15;186(4):2372-81. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002558. Epub 2011 Jan 10. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21220696 Free PMC article.
-
Myeloid Src kinases regulate phagocytosis and oxidative burst in pneumococcal meningitis by activating NADPH oxidase.J Leukoc Biol. 2008 Oct;84(4):1141-50. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0208118. Epub 2008 Jul 14. J Leukoc Biol. 2008. PMID: 18625913 Free PMC article.
-
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced macrophage activation and signal transduction in the absence of Src-family kinases Hck, Fgr, and Lyn.J Exp Med. 1997 May 5;185(9):1661-70. doi: 10.1084/jem.185.9.1661. J Exp Med. 1997. PMID: 9151903 Free PMC article.
-
Hematopoietic cell kinase (HCK) as a therapeutic target in immune and cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2015 Jun 30;6(18):15752-71. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4199. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26087188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple roles of Lyn kinase in myeloid cell signaling and function.Immunol Rev. 2009 Mar;228(1):23-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00758.x. Immunol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19290919 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
STAT4-dependent and -independent Th2 responses correlate with protective immunity against lung infection with Pneumocystis murina.J Immunol. 2013 Jun 15;190(12):6287-94. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300431. Epub 2013 May 6. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23650614 Free PMC article.
-
HCK is a Potential Prognostic Biomarker that Correlates with Immune Cell Infiltration in Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Dis Markers. 2022 Mar 4;2022:3199589. doi: 10.1155/2022/3199589. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 35280440 Free PMC article.
-
Classical versus alternative macrophage activation: the Ying and the Yang in host defense against pulmonary fungal infections.Mucosal Immunol. 2014 Sep;7(5):1023-35. doi: 10.1038/mi.2014.65. Epub 2014 Jul 30. Mucosal Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25073676 Review.
-
Identification of mRNA biomarkers in extremely early hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage (HICH).Proteome Sci. 2024 Nov 30;22(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s12953-024-00237-w. Proteome Sci. 2024. PMID: 39616335 Free PMC article.
-
A panel of seven immune-related genes can serve as a good predictive biomarker for cervical squamous cell carcinoma.Front Genet. 2022 Nov 2;13:1024508. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1024508. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36406134 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abram, C. L., and C. A. Lowell. 2007. The expanding role for ITAM-based signaling pathways in immune cells. Sci. STKE 377re2. - PubMed
-
- Ariizumi, K., G. L. Shen, S. Shikano, S. Xu, R. Ritter, T. Kumamoto, D. Edelbaum, A. Morita, P. R. Bergstresser, and A. Takashima. 2000. Identification of a novel, dendritic cell-associated molecule, dectin-1, by subtractive cDNA cloning. J. Biol. Chem. 27520157-20167. - PubMed
-
- Beavitt, S. E., K. W. Harder, J. M. Kemp, J. Jones, C. Quilici, F. Casagranda, E. Lam, D. Turner, S. Brennan, P. D. Sly, D. M. Tarlinton, G. P. Anderson, and M. L. Hibbs. 2005. Lyn-deficient mice develop severe, persistent asthma: Lyn is a critical negative regulator of Th2 immunity. J. Immunol. 1751867-1875. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

