Staphylococcus aureus superantigens elicit redundant and extensive human Vbeta patterns
- PMID: 19255190
- PMCID: PMC2681734
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01388-08
Staphylococcus aureus superantigens elicit redundant and extensive human Vbeta patterns
Abstract
Staphylococcus aureus can produce a wide variety of exotoxins, including toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 (TSST-1), staphylococcal enterotoxins, and staphylococcal enterotoxin-like toxins. These toxins share superantigenic activity. To investigate the beta chain (Vbeta) specificities of each of these toxins, TSST-1 and all known S. aureus enterotoxins and enterotoxin-like toxins were produced as recombinant proteins and tested for their ability to induce the selective in vitro expansion of human T cells bearing particular Vbeta T-cell receptors (TCR). Although redundancies were observed between the toxins and the Vbeta populations, each toxin induced the expansion of distinct Vbeta subsets, including enterotoxin H and enterotoxin-like toxin J. Surprisingly, the Vbeta signatures were not associated with a specific phylogenic group of toxins. Interestingly, each human Vbeta analyzed in this study was stimulated by at least one staphylococcal superantigen, suggesting that the bacterium derives a selective advantage from targeting the entire human TCR Vbeta panel.
Figures
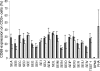
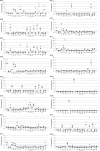


References
-
- Baba, T., F. Takeuchi, M. Kuroda, H. Yuzawa, K. Aoki, A. Oguchi, Y. Nagai, N. Iwama, K. Asano, T. Naimi, H. Kuroda, L. Cui, K. Yamamoto, and K. Hiramatsu. 2002. Genome and virulence determinants of high virulence community-acquired MRSA. Lancet 3591819-1827. - PubMed
-
- Bergdoll, M. S., M. J. Surgalla, and G. M. Dack. 1959. Staphylococcal enterotoxin. I. Purification. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 8562-69. - PubMed
-
- Bohach, G. A. 2006. Staphylococcus aureus exotoxins, p. 464-477. In V. A. Fischetti, R. P. Novick, J. J. Ferreti, D. A. Portnoy, and J. I. Rood (ed.), Gram-positive pathogens, 2nd ed. ASM Press, Washington, DC.
-
- Boisset, S., T. Geissmann, E. Huntzinger, P. Fechter, N. Bendridi, M. Possedko, C. Chevalier, A. C. Helfer, Y. Benito, A. Jacquier, C. Gaspin, F. Vandenesch, and P. Romby. 2007. Staphylococcus aureus RNAIII coordinately represses the synthesis of virulence factors and the transcription regulator Rot by an antisense mechanism. Genes Dev. 211353-1366. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

