Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of sorafenib in patients with hepatic or renal dysfunction: CALGB 60301
- PMID: 19255312
- PMCID: PMC2668705
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2008.20.0931
Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of sorafenib in patients with hepatic or renal dysfunction: CALGB 60301
Abstract
Purpose: We sought to characterize the pharmacokinetics (PK) and determine a tolerable dose of oral sorafenib in patients with hepatic or renal dysfunction.
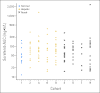
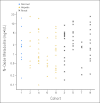
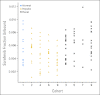
Patients and methods: Patients were assigned to one of nine cohorts: cohort 1, bilirubin < or = upper limit of normal (ULN) and AST < or = ULN and creatinine clearance (CC) > or = 60 mL/min; cohort 2, bilirubin more than ULN but < or = 1.5x ULN and/or AST more than ULN; cohort 3, CC between 40 and 59 mL/min; cohort 4, bilirubin more than 1.5x ULN to < or = 3x ULN (any AST); cohort 5, CC between 20 and 39 mL/min; cohort 6, bilirubin more than 3x ULN to 10x ULN (any AST); cohort 7, CC less than 20 mL/min; cohort 8, albumin less than 2.5 mg/dL (any bilirubin/AST); and cohort 9, hemodialysis. Sorafenib was administered as a 400-mg dose on day 1 for PK, and continuous daily dosing started on day 8.
Results: Of 150 registered patients, 138 patients were treated. With the exception of cohorts 6 and 7, at least 12 patients per cohort were assessable, and the dose level with prospectively defined dose-limiting toxicity in less than one third of patients by day 29 was considered tolerable. No significant associations between the sorafenib PK and cohort were found.
Conclusion: We recommend the following empiric sorafenib starting doses by cohort: cohort 1, 400 mg twice a day; cohort 2, 400 mg twice a day; cohort 3, 400 mg twice a day; cohort 4, 200 mg twice a day; cohort 5, 200 mg twice a day; cohort 6, not even 200 mg every third day tolerable; cohort 7, not defined; cohort 8, 200 mg each day; and cohort 9, 200 mg each day.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Beeram M, Patnaik A, Rowinsky EK. Raf: A strategic target for therapeutic development against cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:6771–6790. - PubMed
-
- Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, et al. BAY 43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and targets the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2004;64:7099–7109. - PubMed
-
- Carlomagno F, Anaganti S, Guida T, et al. BAY 43-9006 inhibition of oncogenic RET mutants. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98:326–334. - PubMed
-
- Ratain MJ, Eisen T, Stadler WM, et al. Phase II placebo-controlled randomized discontinuation trial of sorafenib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:2505–2512. - PubMed
-
- Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM, et al. Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:125–134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U10 CA047577/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA02599/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA47577/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA41287/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA033601/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA077597/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA023108/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA041287/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA04326/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA77658/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA047642/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA31983/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA33601/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA77597/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA11789/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA077658/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA03927/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA031946/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA77651/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA047559/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA077651/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA47559/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA47642/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA31946/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA003927/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources