Increased MET gene copy number negatively affects survival of surgically resected non-small-cell lung cancer patients
- PMID: 19255323
- PMCID: PMC3341799
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2008.19.1635
Increased MET gene copy number negatively affects survival of surgically resected non-small-cell lung cancer patients
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the prognostic role of genomic gain for MET and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) genes in surgically resected non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Patients and methods: This retrospective study included 447 NSCLC patients with available tumor tissue from primary lung tumor and survival data. EGFR and MET status was evaluated by fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) in tissue microarray sections.
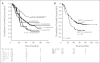
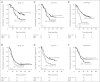
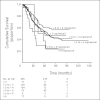
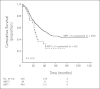
Results: EGFR FISH results were obtained in 376 cases. EGFR gene amplification and high polysomy (EGFR FISH+) were observed in 10.4% and 32.4% of cases, respectively. EGFR FISH-positive patients had a nonsignificant shorter survival than EGFR FISH-negative patients (P = .4). Activating EGFR mutations were detected in 9.7% of 144 stage I-II disease with no impact on survival. MET FISH analysis was performed in 435 cases. High MET gene copy number (mean > or = 5 copies/cell) was observed in 48 cases (MET+, 11.1%), including 18 cases with true gene amplification (4.1%). MET+ status was associated with advanced stage (P = .01), with grade 3 (P = .016) and with EGFR FISH+ result (P < .0001). No patient with activating EGFR mutation resulted MET+. In the whole population, MET-positive patients had shorter survival than MET-negative patients (P = .005). Multivariable model confirmed that MET-negative patients had a significant reduction in the risk of death than MET-positive patients (hazard ratio, 0.66; P = .04).
Conclusion: MET increased gene copy number is an independent negative prognostic factor in surgically resected NSCLC. EGFR gene gain does not impact survival after resection.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Cohen S. Isolation of mouse submaxillary gland protein accelerating incisor eruption and eyelid opening in the new-born animal. J Biol Chem. 1962;237:1555–1562. - PubMed
-
- Pirker R, Szczesna A, von Pawel J, et al. FLEX: A randomized, multicenter, phase III study of cetuximab in combination with cisplatin/vinorelbine (CV) versus CV alone in the first-line treatment of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(suppl):6s. abstr 3.
-
- Shepherd FA, Rodrigues Pereira J, et al. Erlotinib in previously treated non-small cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:123–132. - PubMed
-
- Paez JG, Jänne PA, Lee JC, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: Correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304:1497–1500. - PubMed
-
- Cappuzzo F, Hirsch FR, Rossi E, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor gene and protein and gefitinib sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97:643–655. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

