Diagnostic ultrasound combined with glycoprotein IIb/IIIa-targeted microbubbles improves microvascular recovery after acute coronary thrombotic occlusions
- PMID: 19255341
- PMCID: PMC2752829
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.825067
Diagnostic ultrasound combined with glycoprotein IIb/IIIa-targeted microbubbles improves microvascular recovery after acute coronary thrombotic occlusions
Abstract
Background: The high mechanical index (MI) impulses from a diagnostic ultrasound transducer may be a method of recanalizing acutely thrombosed vessels if the impulses are applied only when microbubbles are channeling through the thrombus.
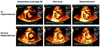
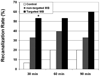
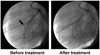
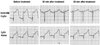
Methods and results: In 45 pigs with acute left anterior descending thrombotic occlusions, a low-MI pulse sequence scheme (contrast pulse sequencing) was used to image the myocardium and guide the delivery of high-MI (1.9 MI) impulses during infusion of either intravenous platelet-targeted microbubbles or nontargeted microbubbles. A third group received no diagnostic ultrasound and microbubbles. All groups received half-dose recombinant prourokinase, heparin, and aspirin. Contrast pulse sequencing examined replenishment of contrast within the central portion of the risk area and guided the application of high-MI impulses. Angiographic recanalization rates, resolution of ST-segment elevation on ECG, and wall thickening were analyzed. Pigs receiving platelet-targeted microbubbles had more rapid replenishment of the central portion of the risk area (80% versus 40% for nontargeted microbubbles; P=0.03) and higher epicardial recanalization rates (53% versus 7% for prourokinase alone; P=0.01). Replenishment of contrast within the risk area (whether with platelet-targeted microbubbles or nontargeted microbubbles) was associated with both higher recanalization rates and even higher rates of ST-segment resolution (82% versus 21% for prourokinase alone; P=0.006). ST-segment resolution occurred in 6 pigs (40%) treated with microbubbles who did not have epicardial recanalization, of which 5 had recovery of wall thickening.
Conclusions: Intravenous platelet-targeted microbubbles combined with brief high-MI diagnostic ultrasound impulses guided by contrast pulse sequencing improve both epicardial recanalization rates and microvascular recovery.
Figures


Comment in
-
Sonothrombolysis: a universally applicable and better way to treat acute myocardial infarction and stroke? Who is going to fund the research?Circulation. 2009 Mar 17;119(10):1358-60. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.846113. Epub 2009 Mar 2. Circulation. 2009. PMID: 19255337 No abstract available.
References
-
- Waxman S, Mittleman MA, Zarich SW, Fitzpatrick PJ, Lewis SM, Leeman DE, Shubrooks SJ, Jr, Snyder JT, Muller JE, Nesto RW. Angioscopic assessment of coronary lesions underlying thrombus. Am J Cardiol. 1997;79:1106–1109. - PubMed
-
- Ueda Y, Asakura M, Hirayama A, Komamura K, Hori M, Komada K. Intracoronary morphology of culprit lesions after reperfusion in acute myocardial infarction: serial angioscopic observations. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1996;27:606–610. - PubMed
-
- Thieme T, Wernecke KD, Meyer R, Brandenstein E, Habedank D, Hinz A, Felix SB, Baumann G, Kleber FX. Angioscopic evaluation of atherosclerotic plaques: validation by histomorphologic analysis and association with stable and unstable coronary syndromes. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1996;28:1–6. - PubMed
-
- AIMS Trial Study Group. Effect of intravenous APSAC on mortality after acute myocardial infarction: Preliminary report of a placebo-controlled clinical trialLancet. Lancet. 1988;1:545–549. - PubMed
-
- ISIS-2 (Second International Study of Infarct Survival) Collaborative Group. Randomized trial of intravenous streptokinanse, oral aspirin, bothof neither among 17,187 cases of suspected acute myocardial infarction: ISIS-2. Lancet. 1988;2:349–360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

