Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of coumarins from the roots of Ferulago campestris (Apiaceae)
- PMID: 19255552
- PMCID: PMC6253837
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules14030939
Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of coumarins from the roots of Ferulago campestris (Apiaceae)
Abstract
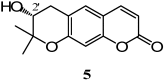
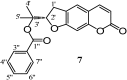
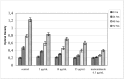
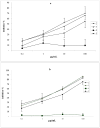
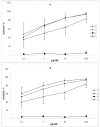
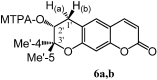
We report the isolation of several coumarins and the stereochemical assessment of some pyranocoumarins, as well as the antibacterial and antioxidant activities of the three most abundant ones (grandivittin, agasyllin and aegelinol benzoate) isolated from the roots of Ferulago campestris collected in Sicily and of the hydrolysis product (aegelinol). Aegelinol and agasyllin showed antibacterial activity against nine ATCC and the same clinically isolated Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial strains. At a concentration between 16 and 125 mg/mL both coumarins showed a significant antibacterial effect against both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. In particular the ATCC strains Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella thypii, Enterobacter cloacae and Enterobacter earogenes (MIC = 16 and 32 mg/mL for aegelinol and agasyllin, respectively) were the most inhibited. Antibacterial activity was also found against Helicobacter pylori: a dose-dependent inhibition was shown between 5 and 25 mg/mL. The antioxidant activity of the coumarins was evaluated by their effects on human whole blood leukocytes (WB) and on isolated polymorphonucleate (PMN) chemiluminescence (CL), PMA-stimulated and resting.
Figures


References
-
- Boulus L. Medicinal plants of North-Africa MI. Algonae; Michigan, USA: 1983. p. 183.
-
- Rosselli S., Maggio A., Eiroa C., Formisano C., Bruno M., Irace C., Maffettone C., Mascolo N. Cytotoxic activity of diterpenoids isolated from the aerial parts of Elaeoselinum asclepium (L.) Bertol. subsp. meoides (Desf.) Fiori (Apiaceae) Planta Med. 2008;74:1285–1287. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1074579. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rosselli S., Maggio A., Formisano C., Napolitano F., Senatore F., Spadaro V., Bruno M. Chemical composition and antibacterial activity of extracts of Helleborus bocconei Ten. subsp. intermedius. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2007;2:675–679.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

