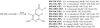Carbonate and carbamate derivatives of 4-demethylpenclomedine as novel anticancer agents
- PMID: 19255760
- PMCID: PMC2717391
- DOI: 10.1007/s00280-009-0933-9
Carbonate and carbamate derivatives of 4-demethylpenclomedine as novel anticancer agents
Abstract
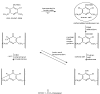
Purpose: The purpose of this investigation was to synthesize a series of carbonate and carbamate derivatives of 4-demethylpenclomedine (DM-PEN), the major plasma non-toxic metabolite of penclomedine (PEN) seen in patients. DM-PEN has been observed to be an active antitumor agent in mouse human xenograft tumor models and non-neurotoxic in a rat model, however, activity in intracranially implanted human glioma xenograft models have not been reported. The major goal was to identify derivatives that are active in brain tumors.
Methods: Derivatives were prepared from DM-PEN and evaluated in vivo against human U251 glioblastoma, D54 glioblastoma and MX-1 breast tumor xenografts and mammary tumor 16/C that were implanted in the mammary fat pad or intracranially (IC).
Results: Carbonate and carbamate derivatives were found to be superior to DM-PEN against IC growing human glioblastoma xenografts.
Conclusion: The activity of the carbonates and carbamates against human tumor xenografts in vivo suggests consideration of these two series of derivatives of DM-PEN for clinical development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Thiolo-, thiono- and dithiocarbonate and thiocarbamate derivatives of demethylpenclomedine as novel anticancer agents.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2006 Jan;57(2):180-4. doi: 10.1007/s00280-005-0031-6. Epub 2005 Aug 11. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16096790
-
4-Demethylpenclomedine, an antitumor-active, potentially nonneurotoxic metabolite of penclomedine.Cancer Res. 1997 Mar 1;57(5):815-7. Cancer Res. 1997. PMID: 9041177
-
Acyl derivatives of demethylpenclomedine, an antitumor-active, non-neurotoxic metabolites of penclomedine.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2001 Jul;48(1):47-52. doi: 10.1007/s002800000255. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11488524
-
An Update of Transition Metal-Catalyzed Decarboxylative Transformations of Cyclic Carbonates and Carbamates.Molecules. 2019 Oct 31;24(21):3930. doi: 10.3390/molecules24213930. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31683557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Of mice and men: values and liabilities of the athymic nude mouse model in anticancer drug development.Eur J Cancer. 2004 Apr;40(6):827-36. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2003.11.028. Eur J Cancer. 2004. PMID: 15120038 Review.
Cited by
-
Glioblastoma: Current Status, Emerging Targets, and Recent Advances.J Med Chem. 2022 Jul 14;65(13):8596-8685. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c01946. Epub 2022 Jul 5. J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35786935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of recurrent metastatic uterine leiomyosarcoma of the spine: a multimodality approach using resection, radiosurgery, and chemotherapy.J Neurosurg Spine. 2015 Nov;23(5):607-612. doi: 10.3171/2015.1.SPINE14640. Epub 2015 Jul 17. J Neurosurg Spine. 2015. PMID: 26186448 Free PMC article.
-
The big picture on nanomedicine: the state of investigational and approved nanomedicine products.Nanomedicine. 2013 Jan;9(1):1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2012.05.013. Epub 2012 Jun 6. Nanomedicine. 2013. PMID: 22684017 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9508201', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9508201/'}]}
- Berlin J, Stewart JA, Storer B, Tutsch KD, Arzoomanian RZ, Alberti D, Feierabend C, Simon K, Wilding G (1998) Phase I clinical and pharmacokinetic trial of penclomedine using a novel, two stage trial design for patients with advanced malignancy. J Clin Oncol 16:1142–1149 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9164209', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9164209/'}]}
- O’Reilly S, Grochow L, Donehower RC, Bowling K, Chen TL, Hartman N, Struck R, Rowinsky EK (1997) Phase I and pharmacologic studies of penclomedine, a novel alkylating agent in patients with solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 15:1974–1984 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC2149952', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2149952/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9514062', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9514062/'}]}
- Jodrell DI, Bowman A, Stewart M, Dunlop N, French R, MacLellan A, Cummings J, Smyth JF (1998) Dose-limiting neurotoxicity in a phase I study of penclomedine (NSC 388720, CRC 88-04), a synthetic alpha-picoline derivative, administered intravenously. Br J Cancer 77:808–811 - PMC - PubMed
-
- None
- Berlin J, Wahamaki A, Tutsch KD, Alberti D, Feierabend C, Binger K, Arzoomanian RZ, Volkman J, Karca J, Mornocha R, Stewart J, Wilding G (1999) Phase I, pharmacokinetic and bioavailability study of oral penclomedine administered daily × 5 every four weeks. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res 40:92
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9816256', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9816256/'}]}
- Hartman NR, O’Reilly S, Rowinsky EK, Collins JM, Strong JM (1996) Murine and human in vivo penclomedine metabolism. Clin Cancer Res 2:953–962 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources