High medium-term survival of Zweymüller SLR-plus stem used in femoral revision
- PMID: 19255816
- PMCID: PMC2706349
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999-009-0760-7
High medium-term survival of Zweymüller SLR-plus stem used in femoral revision
Abstract
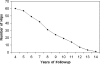
Revision after failed THA resulting from loosening of the femoral component can be challenging even for experienced surgeons. Aseptic loosening usually is associated with some degree of bone loss. We asked whether the Zweymüller SLR-Plus((R)), along with allograft reconstruction of the deficient femoral bone stock, would provide survivorship, osseointegration, and stability similar to or better than previously reported implants for femoral revision. We retrospectively reviewed 69 selected patients (70 hips) who underwent revision of the femoral component using the SLR-Plus((R)) stem during a 10-year period. The indications for revision included aseptic and septic failure of biologic fixation, incorrect implantation, and periprosthetic fracture. Seven patients died and four were lost to followup. Fifty-eight of the 69 patients (59 hips) were available at a mean 8.3 +/- 2.7 years (range, 4-14 years) after revision surgery. There were 14 men and 44 women (mean age, 69 years; range, 42-89 years). Four stems (7%) were rerevised. With rerevision for aseptic reasons, the survival at 10 years was 95% (95% confidence interval, 86%-98%). No femoral periprosthetic osteolysis occurred around the stem and 91% of stems appeared stable radiographically (osseointegration, fibrous). Based on the survival data, we believe the SLR-Plus((R)) stems are reliable for patients undergoing hip revision surgery with central bone loss.
Level of evidence: Level IV, therapeutic study. See the Guidelines for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.
Figures





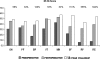
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1097/00003086-200403000-00002', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1097/00003086-200403000-00002'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '7127949', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7127949/'}]}
- Amstutz HC, Ma SM, Jinnah RH, Mai L. Revision of aseptic loose total hip arthroplasties. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;420:2–9. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/S0009-9260(60)80012-8', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/s0009-9260(60)80012-8'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '14408427', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14408427/'}]}
- Barnett E, Nordin BE. The radiological diagnosis of osteoporosis: a new approach. Clin Radiol. 1960;11:166–174. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '10790656', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10790656/'}]}
- Barrack RL, Folgueras AJ. Revision total hip arthroplasty: the femoral component. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1995;3:79–85. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1054/arth.2002.32463', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1054/arth.2002.32463'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12068426', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12068426/'}]}
- Berry DJ. Femoral revision: distal fixation with fluted, tapered grit-blasted stems. J Arthroplasty. 2002;17(suppl 1):142–146. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '7554627', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7554627/'}]}
- Berry DJ, Harmsen WS, Ilstrup D, Lewallen DG, Cabanela ME. Survivorship of uncemented proximally porous-coated femoral components. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995;319:168–177. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

