Using two fluorescent probes to dissect the binding, insertion, and dimerization kinetics of a model membrane peptide
- PMID: 19256494
- PMCID: PMC2667230
- DOI: 10.1021/ja809007f
Using two fluorescent probes to dissect the binding, insertion, and dimerization kinetics of a model membrane peptide
Abstract
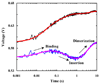
Helix-helix association within a membrane environment represents one of the fundamental processes in membrane protein folding. However, studying the kinetics of such processes has been difficult because most membrane proteins are insoluble in aqueous solution. Here we present a stopped-flow fluorescence study of the membrane-interaction kinetics of a designed, water-soluble transmembrane (TM) peptide, anti-alpha(IIb), which is known to dimerize in phospholipid bilayers. We show that by using two fluorescent amino acids, tryptophan and p-cyanophenylalanine, we are able to kinetically dissect distinct phases in the peptide-membrane interaction, representing membrane binding, membrane insertion, and TM helix-helix association. Our results further show that the last process occurs on a time scale of seconds, indicating that the association of two TM helices is an intrinsically slow event.
Figures

References
-
- Lorch M, Booth PJ. J. Mol. Biol. 2004;344:1109–1121. - PubMed
-
- Nymeyer H, Woolf TB, Garcia AE. Proteins. 2005;59:783–790. - PubMed
- Bond PJ, Sansom MSP. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006;128:2697–2704. - PMC - PubMed
- Lopez CF, Nielsen SO, Srinivas G, DeGrado WF, Klein ML. J. Chem. Theory and Comput. 2006;2:649–655. - PMC - PubMed
- Bu L, Im W, Brooks CL. Biophys. J. 2007;92:854–863. - PMC - PubMed
- Chu JW, Voth GA. Biophys. J. 2007;93:3860–3871. - PMC - PubMed
- Lee J, Im W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008;130:6456–6462. - PubMed
-
- Yin H, Slusky JS, Berger BW, Walters RS, Vilaire G, Rustem LI, Lear JD, Caputo GA, Bennett JS, DeGrado WF. Science. 2007;315:1817–1822. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

