Uridine-based inhibitors as new leads for antibiotics targeting Escherichia coli LpxC
- PMID: 19256534
- PMCID: PMC2709817
- DOI: 10.1021/bi900167q
Uridine-based inhibitors as new leads for antibiotics targeting Escherichia coli LpxC
Erratum in
- Biochemistry. 2009 Aug 18;48(32):7776. Hangauer, Matthew J [added]
Abstract
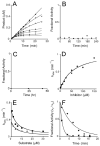
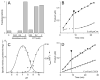
The UDP-3-O-(R-3-hydroxyacyl)-N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase LpxC catalyzes the committed reaction of lipid A (endotoxin) biosynthesis in Gram-negative bacteria and is a validated antibiotic target. Although several previously described compounds bind to the unique acyl chain binding passage of LpxC with high affinity, strategies to target the enzyme's UDP-binding site have not been reported. Here the identification of a series of uridine-based LpxC inhibitors is presented. The most potent examined, 1-68A, is a pH-dependent, two-step, covalent inhibitor of Escherichia coli LpxC that competes with UDP to bind the enzyme in the first step of inhibition. Compound 1-68A exhibits a K(I) of 54 muM and a maximal rate of inactivation (k(inact)) of 1.7 min(-1) at pH 7.4. Dithiothreitol, glutathione and the C207A mutant of E. coli LpxC prevent the formation of a covalent complex by 1-68A, suggesting a role for Cys-207 in inhibition. The inhibitory activity of 1-68A and a panel of synthetic analogues identified moieties necessary for inhibition. 1-68A and a 2-dehydroxy analogue, 1-68Aa, inhibit several purified LpxC orthologues. These compounds may provide new scaffolds for extension of existing LpxC-inhibiting antibiotics to target the UDP binding pocket.
Figures

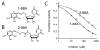




References
-
- Walsh C. Molecular mechanisms that confer antibacterial drug resistance. Nature. 2000;406:775–781. - PubMed
-
- Projan SJ, Youngman PJ. Antimicrobials: new solutions badly needed. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2002;5:463–465. - PubMed
-
- Russell AD, Chopra I. Understanding antibacterial action and resistance. E. Horwood; New York: 1990.
-
- Wyckoff TJ, Raetz CRH, Jackman JE. Antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agents that target endotoxin. Trends Microbiol. 1998;6:154–159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Medical
Miscellaneous

