Effect of excitation wavelength on penetration depth in nonlinear optical microscopy of turbid media
- PMID: 19256688
- PMCID: PMC2868513
- DOI: 10.1117/1.3081544
Effect of excitation wavelength on penetration depth in nonlinear optical microscopy of turbid media
Abstract
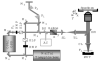
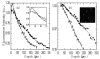
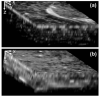
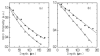
We present a comparative study of two-photon excited fluorescence (TPEF) and second harmonic generation (SHG) imaging in turbid media at 800- and 1300-nm excitation. The depth-dependent decay of TPEF and SHG signals in turbid tissue phantoms is used to estimate the impact of light scattering on excitation intensity at each wavelength. A 50 to 80% increase in scattering length is observed using 1300-nm excitation, while peak TPEF emission intensity is obtained 10 to 20 microm beneath the surface for both sources. The increased penetration depth at 1300 nm is confirmed by TPEF and SHG microscopy of tissue phantoms composed of gelatin/microspheres and 3-D organotypic collagen-fibroblast cultures, respectively. Our results establish the feasibility of 1.3-microm excitation in nonlinear optical microscopy.
Figures
References
-
- Dunn AK, Wallace VP, Coleno M, Berns MW, Tromberg BJ. Influence of optical properties on two-photon fluorescence imaging in turbid samples. Appl. Opt. 2000;39:1194–1201. - PubMed
-
-
Oheim M, Beaurepaire E, Chaigbneau E, Mertz J, Charpak S. Two-photon microscopy in brain tissue: parameters influencing the imaging depth. J. Neurosci. Methods. 2001;111:29–37. also see erratum at Two-photon microscopy in brain tissue: parameters influencing the imaging depth. J. Neurosci. Methods. 2001;112:205.
-
-
- Tang S, Krasieva TB, Chen Z, Tempea G, Tromberg BJ. Effect of pulse duration on two-photon excited fluorescence and second harmonic generation in nonlinear optical microscopy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2006;11:020501–020503. - PubMed
-
- Theer P, Hasan MT, Denk W. Two-photon imaging to a depth of 1000-μm in living brains by use of a Ti:Al2O3 rgenerative amplifier. Opt. Lett. 2003;28:1022–1024. - PubMed
-
- Chu SW, Chen IH, Liu TM, Chen PC, Sun CK. Multimodal nonlinear spectral microscopy based on a femtosecond Cr-:forsterite laser. Opt. Lett. 2001;26:1909–1911. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

