Novel renal replacement strategies for the elimination of serum free light chains in patients with kappa light chain nephropathy
- PMID: 19258212
- PMCID: PMC3351959
- DOI: 10.1186/2047-783x-14-2-47
Novel renal replacement strategies for the elimination of serum free light chains in patients with kappa light chain nephropathy
Abstract
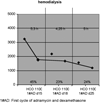
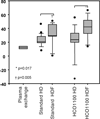
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a malignancy with excessive production of monoclonal proteins. At disease presentation 30% of MM patients have significant renal impairment which may progress to renal failure requiring dialysis. Besides chemotherapy extracorporeal elimination procedures such as plasma exchange have been applied as adjuvant strategies to eliminate free light chains from circulating blood, however the efficacy was poor with older techniques. We report about a highly efficient method to eliminate serum free light chain (sFLC) using a newly designed protein leaking membrane in patients suffering from sFLC induced acute renal failure. The protein leaking membrane (HCO 1100) is characterized by increased pore size facilitating elimination of middle molecules such as sFLC kappa (22.5 kD). The HCO 1100 membrane was applied in a hemodialysis and hemodiafiltration mode and compared to standard procedures (high flux hemodialysis, hemodiafiltration and plasma exchange). Hemodiafiltration with the protein leaking membrane HCO 1100 was superior to all other extracorporeal replacement strategies in eliminating sFLC-kappa from circulating blood. A median blood reduction rate of 40.8% (range 13.9%-66.4%) was achieved during hemodiafiltration. The corresponding peak clearance rate was 25 ml/min. Importantly, the poorest elimination rate was achieved by plasma exchange followed by standard high flux hemodialysis. Extracorporeal elimination strategies with the protein leaking membrane HCO 1100 may be a promising adjuvant treatment strategy for patients with sFLC nephropathy requiring dialysis. Hemodiafiltration and to lesser extend also hemodialysis with the HCO 1100 hemofilter are able to eliminate substantial amounts of sFLC kappa in MM patients.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of Haemodiafiltration with Heat Sterilized High-Flux Polyphenylene HF Dialyzer in Reducing Free Light Chains in Patients with Myeloma Cast Nephropathy.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 14;10(10):e0140463. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140463. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26466100 Free PMC article.
-
Extracorporeal light chain elimination: high cut-off (HCO) hemodialysis parallel to chemotherapy allows for a high proportion of renal recovery in multiple myeloma patients with dialysis-dependent acute kidney injury.Ann Hematol. 2012 May;91(5):729-735. doi: 10.1007/s00277-011-1383-0. Epub 2011 Dec 15. Ann Hematol. 2012. PMID: 22170517
-
Evaluation of blood purification and bortezomib plus dexamethasone therapy for the treatment of acute renal failure due to myeloma cast nephropathy.Ther Apher Dial. 2010 Oct;14(5):451-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-9987.2010.00863.x. Ther Apher Dial. 2010. PMID: 21175542
-
Light chains removal by extracorporeal techniques in acute kidney injury due to multiple myeloma: a position statement of the Onconephrology Work Group of the Italian Society of Nephrology.J Nephrol. 2016 Dec;29(6):735-746. doi: 10.1007/s40620-016-0347-9. Epub 2016 Oct 18. J Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27757797 Review.
-
The use of different dialysis membranes in therapy of patients with multiple myeloma.Polim Med. 2019 Jul-Dec;49(2):67-70. doi: 10.17219/pim/122014. Polim Med. 2019. PMID: 32544311 Review.
Cited by
-
Bendamustine in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma.Eur J Med Res. 2010 Jan 29;15(1):13-9. doi: 10.1186/2047-783x-15-1-13. Eur J Med Res. 2010. PMID: 20159666 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic monitoring of M-protein quantification by immunotyping using capillary zone electrophoresis during the chemotherapy of patients with multiple myeloma.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 4;15(1):11541. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-96565-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40185913 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

