Pivotal roles of the outer membrane polysaccharide export and polysaccharide copolymerase protein families in export of extracellular polysaccharides in gram-negative bacteria
- PMID: 19258536
- PMCID: PMC2650888
- DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.00024-08
Pivotal roles of the outer membrane polysaccharide export and polysaccharide copolymerase protein families in export of extracellular polysaccharides in gram-negative bacteria
Abstract
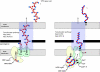
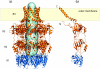
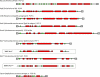
Many bacteria export extracellular polysaccharides (EPS) and capsular polysaccharides (CPS). These polymers exhibit remarkably diverse structures and play important roles in the biology of free-living, commensal, and pathogenic bacteria. EPS and CPS production represents a major challenge because these high-molecular-weight hydrophilic polymers must be assembled and exported in a process spanning the envelope, without compromising the essential barrier properties of the envelope. Emerging evidence points to the existence of molecular scaffolds that perform these critical polymer-trafficking functions. Two major pathways with different polymer biosynthesis strategies are involved in the assembly of most EPS/CPS: the Wzy-dependent and ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter-dependent pathways. They converge in an outer membrane export step mediated by a member of the outer membrane auxiliary (OMA) protein family. OMA proteins form outer membrane efflux channels for the polymers, and here we propose the revised name outer membrane polysaccharide export (OPX) proteins. Proteins in the polysaccharide copolymerase (PCP) family have been implicated in several aspects of polymer biogenesis, but there is unequivocal evidence for some systems that PCP and OPX proteins interact to form a trans-envelope scaffold for polymer export. Understanding of the precise functions of the OPX and PCP proteins has been advanced by recent findings from biochemistry and structural biology approaches and by parallel studies of other macromolecular trafficking events. Phylogenetic analyses reported here also contribute important new insight into the distribution, structural relationships, and function of the OPX and PCP proteins. This review is intended as an update on progress in this important area of microbial cell biology.
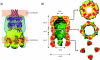
Figures



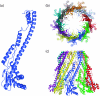


References
-
- Akama, H., T. Matsuura, S. Kashiwagi, H. Yoneyama, S. Narita, T. Tsukihara, A. Nakagawa, and T. Nakae. 2004. Crystal structure of the membrane fusion protein, MexA, of the multidrug transporter in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Biol. Chem. 27925939-25942. - PubMed
-
- Arrecubieta, C., T. C. Hammarton, B. Barrett, S. Chareonsudjai, N. Hodson, D. Rainey, and I. S. Roberts. 2001. The transport of group 2 capsular polysaccharides across the periplasmic space in Escherichia coli. Roles for the KpsE and KpsD proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2764245-4250. - PubMed
-
- Bastin, D. A., G. Stevenson, P. K. Brown, A. Haase, and P. R. Reeves. 1993. Repeat unit polysaccharides of bacteria: a model for polymerization resembling that of ribosomes and fatty acid synthetase, with a novel mechanism for determining chain length. Mol. Microbiol. 7725-734. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

