Conditional deletion of STAT5 in adult mouse hematopoietic stem cells causes loss of quiescence and permits efficient nonablative stem cell replacement
- PMID: 19258595
- PMCID: PMC2686137
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2008-09-181107
Conditional deletion of STAT5 in adult mouse hematopoietic stem cells causes loss of quiescence and permits efficient nonablative stem cell replacement
Abstract
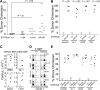
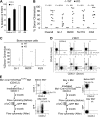
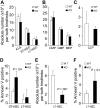
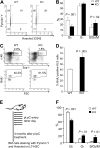
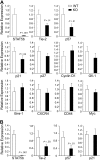
Currently, there is a major need in hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) transplantation to develop reduced-intensity regimens that do not cause DNA damage and associated toxicities and that allow a wider range of patients to receive therapy. Cytokine receptor signals through c-Kit and c-Mpl can modulate HSC quiescence and engraftment, but the intracellular signals and transcription factors that mediate these effects during transplantation have not been defined. Here we show that loss of one allele of signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5) in nonablated adult mutant mice permitted engraftment with wild-type HSC. Conditional deletion of STAT5 using Mx1-Cre caused maximal reduction in STAT5 mRNA (> 97%) and rapidly decreased quiescence-associated c-Mpl downstream targets (Tie-2, p57), increased HSC cycling, and gradually reduced survival and depleted the long-term HSC pool. Host deletion of STAT5 was persistent and permitted efficient donor long-term HSC engraftment in primary and secondary hosts in the absence of ablative conditioning. Overall, these studies establish proof of principle for targeting of STAT5 as novel transplantation conditioning and demonstrate, for the first time, that STAT5, a mitogenic factor in most cell types, including hematopoietic progenitors, is a key transcriptional regulator that maintains quiescence of HSC during steady-state hematopoiesis.
Figures
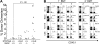

References
-
- Nijnik A, Woodbine L, Marchetti C, et al. DNA repair is limiting for haematopoietic stem cells during ageing. Nature. 2007;447:686–690. - PubMed
-
- Down JD, Ploemacher RE. Transient and permanent engraftment potential of murine hematopoietic stem cell subsets: differential effects of host conditioning with gamma radiation and cytotoxic drugs. Exp Hematol. 1993;21:913–921. - PubMed
-
- Micklem HS, Clarke CM, Evans EP, Ford CE. Fate of chromosome-marked mouse bone marrow cells tranfused into normal syngeneic recipients. Transplantation. 1968;6:299–302. - PubMed
-
- Nilsson SK, Dooner MS, Tiarks CY, Weier HU, Quesenberry PJ. Potential and distribution of transplanted hematopoietic stem cells in a nonablated mouse model. Blood. 1997;89:4013–4020. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

