Continuous depth-of-interaction encoding using phosphor-coated scintillators
- PMID: 19258685
- PMCID: PMC2748919
- DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/54/6/023
Continuous depth-of-interaction encoding using phosphor-coated scintillators
Abstract
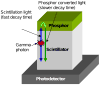
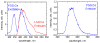
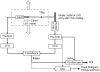
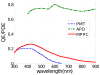
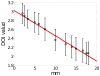
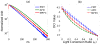
We investigate a novel detector using a lutetium oxyorthosilicate (LSO) scintillator and YGG (yttrium-aluminum-gallium oxide:cerium, Y(3)(Al,Ga)(5)O(12):Ce) phosphor to construct a detector with continuous depth-of-interaction (DOI) information. The far end of the LSO scintillator is coated with a thin layer of YGG phosphor powder which absorbs some fraction of the LSO scintillation light and emits wavelength-shifted photons with a characteristic decay time of approximately 50 ns. The near end of the LSO scintillator is directly coupled to a photodetector. The photodetector detects a mixture of the LSO light and the light emitted by YGG. With appropriate placement of the coating, the ratio of the light converted from the YGG coating with respect to the unconverted LSO light can be made to depend on the interaction depth. DOI information can then be estimated by inspecting the overall light pulse decay time. Experiments were conducted to optimize the coating method. 19 ns decay time differences across the length of the detector were achieved experimentally when reading out a 1.5 x 1.5 x 20 mm(3) LSO crystal with unpolished surfaces and half-coated with YGG phosphor. The same coating scheme was applied to a 4 x 4 LSO array. Pulse shape discrimination (PSD) methods were studied to extract DOI information from the pulse shape changes. The DOI full-width-half-maximum (FWHM) resolution was found to be approximately 8 mm for this 2 cm thick array.
Figures
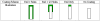







References
-
- Chandrikamohan P, DeVol TA. Comparison of Pulse Shape Discrimination Methods for Phoswich and CsI:Tl Detectors. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2007;54:398–403.
-
- Du H, Yang Y, Cherry SR. Measurements of wavelength shifting (WLS) fibre readout for a highly multiplexed, depth-encoding PET detector. Phys Med Biol. 2007;52:2499–514. - PubMed
-
- Judenhofer MS, Pichler BJ, Cherry SR. Evaluation of high performance data acquisition boards for simultaneous sampling of fast signals from PET detectors. Phys Med Biol. 2005;50:29–44. - PubMed
-
- Liu H, Omura T, Watanabe M, Yamashita T. Development of a depth of interaction detector for [gamma]-rays. Nucl Instrum Methods A. 2001;459:182–90.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
