Dietary supplementation with a specific combination of high protein, leucine, and fish oil improves muscle function and daily activity in tumour-bearing cachectic mice
- PMID: 19259092
- PMCID: PMC2653763
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604905
Dietary supplementation with a specific combination of high protein, leucine, and fish oil improves muscle function and daily activity in tumour-bearing cachectic mice
Erratum in
- Br J Cancer. 2009 Apr 7;100(7):1211
Abstract
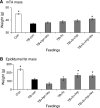
Cancer cachexia is characterised by metabolic alterations leading to loss of adipose tissue and lean body mass and directly compromises physical performance and the quality of life of cancer patients. In a murine cancer cachectic model, the effects of dietary supplementation with a specific combination of high protein, leucine and fish oil on weight loss, muscle function and physical activity were investigated. Male CD2F1 mice, 6-7 weeks old, were divided into body weight-matched groups: (1) control, (2) tumour-bearing, and (3) tumour-bearing receiving experimental diets. Tumours were induced by s.c. inoculation with murine colon adenocarcinoma (C26) cells. Food intake, body mass, tumour size and 24 h-activity were monitored. Then, 20 days after tumour/vehicle inoculation, the animals were killed and muscle function was tested ex vivo. Tumour-bearing mice showed reduced carcass, muscle and fat mass compared with controls. EDL muscle performance and total daily activity were impaired in the tumour-bearing mice. Addition of single nutrients resulted in no or modest effects. However, supplementation of the diet with the all-in combination of high protein, leucine and fish oil significantly reduced loss of carcass, muscle and fat mass (loss in mass 45, 52 and 65% of TB-con, respectively (P<0.02)) and improved muscle performance (loss of max force reduced to 55-64% of TB-con (P<0.05)). Moreover, total daily activity normalised after intervention with the specific nutritional combination (50% of the reduction in activity of TB-con (P<0.05)). In conclusion, a nutritional combination of high protein, leucine and fish oil reduced cachectic symptoms and improved functional performance in cancer cachectic mice. Comparison of the nutritional combination with its individual modules revealed additive effects of the single components provided.
Figures
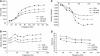

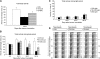
References
-
- Andreyev HJ, Norman AR, Oates J, Cunningham D (1998) Why do patients with weight loss have a worse outcome when undergoing chemotherapy for gastrointestinal malignancies? Eur J Cancer 34: 503–509 - PubMed
-
- Anthony JC, Lang CH, Crozier SJ, Anthony TG, MacLean DA, Kimball SR, Jefferson LS (2002a) Contribution of insulin to the translational control of protein synthesis in skeletal muscle by leucine. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 282: E1092–E1101 - PubMed
-
- Anthony JC, Reiter AK, Anthony TG, Crozier SJ, Lang CH, MacLean DA, Kimball SR, Jefferson LS (2002b) Orally administered leucine enhances protein synthesis in skeletal muscle of diabetic rats in the absence of increases in 4E-BP1 or S6K1 phosphorylation. Diabetes 51: 928–936 - PubMed
-
- Argiles JM (2005) Cancer-associated malnutrition. Eur J Oncol Nurs 9: S39–S50 - PubMed
-
- Baracos VE, Mackenzie ML (2006) Investigations of branched-chain amino acids and their metabolites in animal models of cancer. J Nutr 136: 237S–242S - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

