Tumor stroma derived biomarkers in cancer
- PMID: 19259624
- PMCID: PMC4476244
- DOI: 10.1007/s10555-008-9175-2
Tumor stroma derived biomarkers in cancer
Abstract
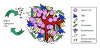
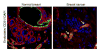
In recent years the importance of the tumor stroma for the development, promotion and invasion of cancer is becoming increasingly clear. Besides a malignantly transformed cancer cell, tumors also contains many other cell types, including endothelial cells, fibroblasts and cells of the immune system. These cells together with the cancer cells produce the sum extracellular matrix (ECM) of the tumor. The ECM and the non-malignant cells of the tumor are defined as the "tumor stroma". Just as the malignant cell itself can be the source of substances that can be used as biomarkers of cancer, the tumor stroma contains factors that potentially can be used as biomarkers when treating patients with cancer. In this review we will discuss the role of the tumor stroma as a source of new cancer biomarkers. This concept highlights a novel view of cancer and treats them as organized organs. Additionally, this further stresses the importance of including factors related to the tumor stroma into the diagnostic and therapeutic equation of cancer.
Figures

References
-
- Kalluri R, Zeisberg M. Fibroblasts in cancer. Nature Reviews Cancer. 2006;6:392–401. - PubMed
-
- Folkman J, Kalluri R. Cancer without disease. Nature. 2004;427:787. - PubMed
-
- Hu M, Yao J, Cai L, Bachman KE, van den Brule F, Velculescu V, et al. Distinct epigenetic changes in the stromal cells of breast cancers. Nature Genetics. 2005;37:899–905. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P, Jain RK. Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature. 2000;407:249–257. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

