Reliability of quantitative sudomotor axon reflex testing and quantitative sensory testing in neuropathy of impaired glucose regulation
- PMID: 19260066
- PMCID: PMC4421877
- DOI: 10.1002/mus.21210
Reliability of quantitative sudomotor axon reflex testing and quantitative sensory testing in neuropathy of impaired glucose regulation
Abstract
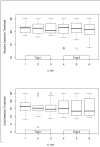
Reproducible neurophysiologic testing paradigms are critical for multicenter studies of neuropathy associated with impaired glucose regulation (IGR), yet the best methodologies and endpoints remain to be established. This study evaluates the reproducibility of neurophysiologic tests within a multicenter research setting. Twenty-three participants with neuropathy and IGR were recruited from two study sites. The reproducibility of quantitative sudomotor axon reflex test (QSART) and quantitative sensory test (QST) (using the CASE IV system) was determined in a subset of patients at two sessions, and it was calculated from intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs). QST (cold detection threshold: ICC=0.80; vibration detection threshold: ICC=0.75) was more reproducible than QSART (ICC foot=0.52). The performance of multiple tests in one setting did not improve reproducibility of QST. QST reproducibility in our IGR patients was similar to reports of other studies. QSART reproducibility was significantly lower than QST. In this group of patients, the reproducibility of QSART was unacceptable for use as a secondary endpoint measure in clinical research trials.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Test-retest reliability of quantitative sudomotor axon reflex testing.J Clin Neurophysiol. 2013 Jun;30(3):308-12. doi: 10.1097/WNP.0b013e3182873254. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2013. PMID: 23733097
-
Diagnostic Criteria for Small Fiber Neuropathy.J Clin Neuromuscul Dis. 2017 Mar;18(3):125-131. doi: 10.1097/CND.0000000000000154. J Clin Neuromuscul Dis. 2017. PMID: 28221302
-
Axon reflex flare and quantitative sudomotor axon reflex contribute in the diagnosis of small fiber neuropathy.Muscle Nerve. 2013 Mar;47(3):357-63. doi: 10.1002/mus.23543. Epub 2012 Nov 24. Muscle Nerve. 2013. PMID: 23180613
-
Technology literature review: quantitative sensory testing.Muscle Nerve. 2004 May;29(5):734-47. doi: 10.1002/mus.20053. Muscle Nerve. 2004. PMID: 15116380 Review.
-
Sweat testing to evaluate autonomic function.Clin Auton Res. 2009 Apr;19(2):79-87. doi: 10.1007/s10286-008-0506-8. Epub 2008 Nov 6. Clin Auton Res. 2009. PMID: 18989618 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Opioid-induced hyperalgesia in community-dwelling adults with chronic pain.Pain. 2015 Jun;156(6):1145-1152. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000170. Pain. 2015. PMID: 25815431 Free PMC article.
-
Accessing autonomic function can early screen metabolic syndrome.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43449. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043449. Epub 2012 Aug 20. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22916265 Free PMC article.
-
Sudomotor Testing of Diabetes Polyneuropathy.Front Neurol. 2018 Sep 26;9:803. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00803. eCollection 2018. Front Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30319533 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis and treatment of pain in small-fiber neuropathy.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2011 Jun;15(3):193-200. doi: 10.1007/s11916-011-0181-7. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2011. PMID: 21286866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How stable are quantitative sensory testing measurements over time? Report on 10-week reliability and agreement of results in healthy volunteers.J Pain Res. 2017 Aug 29;10:2067-2078. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S137391. eCollection 2017. J Pain Res. 2017. PMID: 28919806 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dyck PJ, Davies JL, Litchy WJ, O'Brien PC. Longitudinal assessment of diabetic polyneuropathy using a composite score in the Rochester Diabetic Neuropathy Study cohort. Neurology. 1997 Jul;49(1):229–39. - PubMed
-
- Dyck PJ, Karnes JL, O'Brien PC, Litchy WJ, Low PA, Melton LJ., III The Rochester Diabetic Neuropathy Study: reassessment of tests and criteria for diagnosis and staged severity. Neurology. 1992 Jun;42(6):1164–70. - PubMed
-
- Low PA, Denq JC, Opfer-Gehrking TL, Dyck PJ, O'Brien PC, Slezak JM. Effect of age and gender on sudomotor and cardiovagal function and blood pressure response to tilt in normal subjects. Muscle Nerve. 1997 Dec;20(12):1561–8. - PubMed
-
- Dyck PJ, Davies JL, Litchy WJ, O'Brien PC. Longitudinal assessment of diabetic polyneuropathy using a composite score in the Rochester Diabetic Neuropathy Study cohort. Neurology. 1997 Jul;49(1):229–39. - PubMed
-
- Dyck PJ, Karnes JL, O'Brien PC, Litchy WJ, Low PA, Melton LJ., III The Rochester Diabetic Neuropathy Study: reassessment of tests and criteria for diagnosis and staged severity. Neurology. 1992 Jun;42(6):1164–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 NS038849/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS40458/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K02 NS042056/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 NS07222/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK064814/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 NS007222/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS38849/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- DK02-016/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- NS36778/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 5P60DK-20572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- NS42056/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS036778/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00042/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK064814/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS040458/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000042/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States

