Comparative functional analysis of the Caenorhabditis elegans and Drosophila melanogaster proteomes
- PMID: 19260763
- PMCID: PMC2650730
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000048
Comparative functional analysis of the Caenorhabditis elegans and Drosophila melanogaster proteomes
Abstract
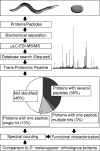
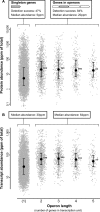
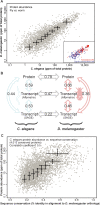
The nematode Caenorhabditis elegans is a popular model system in genetics, not least because a majority of human disease genes are conserved in C. elegans. To generate a comprehensive inventory of its expressed proteome, we performed extensive shotgun proteomics and identified more than half of all predicted C. elegans proteins. This allowed us to confirm and extend genome annotations, characterize the role of operons in C. elegans, and semiquantitatively infer abundance levels for thousands of proteins. Furthermore, for the first time to our knowledge, we were able to compare two animal proteomes (C. elegans and Drosophila melanogaster). We found that the abundances of orthologous proteins in metazoans correlate remarkably well, better than protein abundance versus transcript abundance within each organism or transcript abundances across organisms; this suggests that changes in transcript abundance may have been partially offset during evolution by opposing changes in protein abundance.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests. The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- O'Brien KP, Westerlund I, Sonnhammer EL. OrthoDisease: a database of human disease orthologs. Hum Mutat. 2004;24:112–119. - PubMed
-
- C. elegans Sequencing Consortium. Genome sequence of the nematode C. elegans: a platform for investigating biology. Science. 1998;282:2012–2018. - PubMed
-
- Anderson L, Seilhamer J. A comparison of selected mRNA and protein abundances in human liver. Electrophoresis. 1997;18:533–537. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

