The Cul3/Klhdc5 E3 ligase regulates p60/katanin and is required for normal mitosis in mammalian cells
- PMID: 19261606
- PMCID: PMC2670170
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M809374200
The Cul3/Klhdc5 E3 ligase regulates p60/katanin and is required for normal mitosis in mammalian cells
Abstract
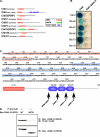
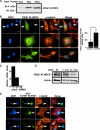
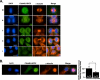
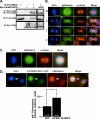
The proper regulation of factors involved in mitosis is crucial to ensure normal cell division. Levels and activities of proteins are regulated in many ways, one of which is ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation. E3 ubiquitin ligases are involved in targeting specific substrates for degradation by facilitating their ubiquitination. In seeking to elucidate additional biological roles for Cul3 we performed a two-hybrid screen and identified Ctb9/KLHDC5 as a Cul3-interacting protein. Overexpression of Ctb9/KLHDC5 resulted in an increase in microtubule density as well as persistent microtubule bridges between post-mitotic cells. Conversely, down-regulation of Ctb9/KLHDC5 showed a pronounced reduction in microtubule density. Based on these observations, we examined the interactions between Cul3, Ctb9/KLHDC5, and the microtubule-severing protein, p60/katanin. Here we show that p60/katanin interacts with a complex consisting of Cul3 and Ctb9/KLHDC5, which results in ubiquitin laddering of p60/katanin. Also, Cul3-deficient cells or Ctb9/KLHDC5-deficient cells show an increase in p60/katanin levels, indicating that Cul3/Ctb9/KLHDC5 is required for efficient p60/katanin removal. We demonstrate a novel regulatory mechanism for p60/katanin that occurs at the level of targeted proteolysis to allow normal mitotic progression in mammalian cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
USP47 and C terminus of Hsp70-interacting protein (CHIP) antagonistically regulate katanin-p60-mediated axonal growth.J Neurosci. 2013 Jul 31;33(31):12728-38. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0698-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23904609 Free PMC article.
-
Two domains of p80 katanin regulate microtubule severing and spindle pole targeting by p60 katanin.J Cell Sci. 2000 May;113 ( Pt 9):1623-33. doi: 10.1242/jcs.113.9.1623. J Cell Sci. 2000. PMID: 10751153
-
Katanin p60 contributes to microtubule instability around the midbody and facilitates cytokinesis in rat cells.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 26;8(11):e80392. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080392. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24303010 Free PMC article.
-
E3 ubiquitin ligases and mitosis: embracing the complexity.Trends Cell Biol. 2008 Feb;18(2):84-94. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2007.12.001. Epub 2008 Jan 22. Trends Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18215523 Review.
-
Current trends of high-risk gene Cul3 in neurodevelopmental disorders.Front Psychiatry. 2023 Jul 28;14:1215110. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1215110. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37575562 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Kelch Repeat and BTB Domain Containing Protein 5 (Kbtbd5) Regulates Skeletal Muscle Myogenesis through the E2F1-DP1 Complex.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jun 12;290(24):15350-61. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.629956. Epub 2015 May 4. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25940086 Free PMC article.
-
The role of katanin p60 in breast cancer bone metastasis.Oncol Lett. 2018 Apr;15(4):4963-4969. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.7942. Epub 2018 Feb 2. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29552132 Free PMC article.
-
USP47 and C terminus of Hsp70-interacting protein (CHIP) antagonistically regulate katanin-p60-mediated axonal growth.J Neurosci. 2013 Jul 31;33(31):12728-38. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0698-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23904609 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Cul3 binding proteins function to remodel E3 ligase complexes.BMC Cell Biol. 2014 Jul 10;15:28. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-15-28. BMC Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 25011449 Free PMC article.
-
Katanin spiral and ring structures shed light on power stroke for microtubule severing.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2017 Sep;24(9):717-725. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.3448. Epub 2017 Aug 7. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28783150 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

