Bortezomib overcomes tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells in part through the inhibition of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway
- PMID: 19261616
- PMCID: PMC2670117
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M806268200
Bortezomib overcomes tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells in part through the inhibition of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway
Abstract
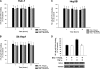
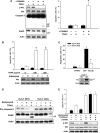
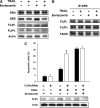
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common and aggressive human malignancies. Recombinant tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is a promising anti-tumor agent. However, many HCC cells show resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. In this study, we showed that bortezomib, a proteasome inhibitor, overcame TRAIL resistance in HCC cells, including Huh-7, Hep3B, and Sk-Hep1. The combination of bortezomib and TRAIL restored the sensitivity of HCC cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Comparing the molecular change in HCC cells treated with these agents, we found that down-regulation of phospho-Akt (P-Akt) played a key role in mediating TRAIL sensitization of bortezomib. The first evidence was that bortezomib down-regulated P-Akt in a dose- and time-dependent manner in TRAIL-treated HCC cells. Second, LY294002, a PI3K inhibitor, also sensitized resistant HCC cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Third, knocking down Akt1 by small interference RNA also enhanced TRAIL-induced apoptosis in Huh-7 cells. Finally, ectopic expression of mutant Akt (constitutive active) in HCC cells abolished TRAIL sensitization effect of bortezomib. Moreover, okadaic acid, a protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) inhibitor, reversed down-regulation of P-Akt in bortezomib-treated cells, and PP2A knockdown by small interference RNA also reduced apoptosis induced by the combination of TRAIL and bortezomib, indicating that PP2A may be important in mediating the effect of bortezomib on TRAIL sensitization. Together, bortezomib overcame TRAIL resistance at clinically achievable concentrations in hepatocellular carcinoma cells, and this effect is mediated at least partly via inhibition of the PI3K/Akt pathway.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Down-regulation of phospho-Akt is a major molecular determinant of bortezomib-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Cancer Res. 2008 Aug 15;68(16):6698-707. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0257. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18701494
-
Synergistic interactions between sorafenib and bortezomib in hepatocellular carcinoma involve PP2A-dependent Akt inactivation.J Hepatol. 2010 Jan;52(1):88-95. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2009.10.011. Epub 2009 Oct 23. J Hepatol. 2010. PMID: 19913321
-
CIP2A mediates effects of bortezomib on phospho-Akt and apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Oncogene. 2010 Nov 25;29(47):6257-66. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.357. Epub 2010 Aug 23. Oncogene. 2010. PMID: 20729919
-
Targeting the extrinsic apoptosis signaling pathway for cancer therapy.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2011 Aug;60(8):1173-80. doi: 10.1007/s00262-011-1008-4. Epub 2011 Apr 6. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2011. PMID: 21626033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma: targeting of oncogenic signaling networks in TRAIL resistant cancer cells.Mol Biol Rep. 2014 Oct;41(10):6909-17. doi: 10.1007/s11033-014-3577-8. Epub 2014 Jul 19. Mol Biol Rep. 2014. PMID: 25037270 Review.
Cited by
-
Superior antitumoral activity of dimerized targeted single-chain TRAIL fusion proteins under retention of tumor selectivity.Cell Death Dis. 2012 Apr 12;3(4):e295. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2012.29. Cell Death Dis. 2012. PMID: 22495350 Free PMC article.
-
Cancerous inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A determines bortezomib-induced apoptosis in leukemia cells.Haematologica. 2013 May;98(5):729-38. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2011.050187. Epub 2012 Sep 14. Haematologica. 2013. PMID: 22983581 Free PMC article.
-
The ubiquitin-proteasome system: opportunities for therapeutic intervention in solid tumors.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2015 Feb;22(1):T1-17. doi: 10.1530/ERC-14-0005. Epub 2014 Mar 21. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2015. PMID: 24659480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
All roads lead to PP2A: exploiting the therapeutic potential of this phosphatase.FEBS J. 2016 Mar;283(6):1004-24. doi: 10.1111/febs.13573. Epub 2015 Nov 14. FEBS J. 2016. PMID: 26507691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mcl-1-dependent activation of Beclin 1 mediates autophagic cell death induced by sorafenib and SC-59 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Cell Death Dis. 2013 Feb 7;4(2):e485. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.18. Cell Death Dis. 2013. PMID: 23392173 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schwartz, M., Roayaie, S., and Konstadoulakis, M. (2007) Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol. 4, 424–432 - PubMed
-
- Takeda, K., Stagg, J., Yagita, H., Okumura, K., and Smyth, M. J. (2007) Oncogene 26, 3745–3757 - PubMed
-
- Sayers, T. J., Brooks, A. D., Koh, C. Y., Ma, W., Seki, N., Raziuddin, A., Blazar, B. R., Zhang, X., Elliott, P. J., and Murphy, W. J. (2003) Blood 102, 303–310 - PubMed
-
- Kim, Y., Suh, N., Sporn, M., and Reed, J. C. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277, 22320–22329 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

