Th17 cells: from precursors to players in inflammation and infection
- PMID: 19261692
- PMCID: PMC2675030
- DOI: 10.1093/intimm/dxp021
Th17 cells: from precursors to players in inflammation and infection
Abstract
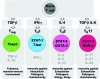
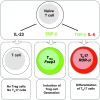
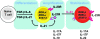
Upon activation, naive CD4(+) T cells differentiate into different lineages of effector T(h) subsets. Each subset is characterized by its unique cytokine profile and biological functions. T(h)17, a newly described T(h) subset that produces IL-17, IL-17F and IL-22 in preference to other cytokines, has been shown to play an important role in clearing specific pathogens and in inducing autoimmune tissue inflammations. Over the last 2-3 years, significant progress has been made to understand the development and biological functions of T(h)17 subset. Transforming growth factor beta (TGF) together with IL-6 or IL-21 initiates the differentiation while IL-23 stabilizes the generation of T(h)17 cells. The transcription factors of T(h)17 cells [retinoid-related orphan receptor (ROR) gammat, ROR-alpha and signal transducer and activator of transcription-3] have been described recently. Since TGF-beta is essential for the generation of both T(h)17 and regulatory T (T(reg)) cells from naive T cells, which suggests a developmental link between T(h)17 and T(reg) cells. Functions of these two subsets of T cells are, however, opposite to each other; T(h)17 cells are highly pathogenic during the inflammatory process while T(reg) cells are crucial for inhibiting tissue inflammation and maintaining self-tolerance. Here, we review the recent information on differentiation and effector functions of T(h)17 cells during inflammatory conditions.
Figures
References
-
- Reiner SL. Development in motion: helper T cells at work. Cell. 2007;129:33. - PubMed
-
- Mosmann TR, Cherwinski H, Bond MW, Giedlin MA, Coffman RL. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J. Immunol. 1986;136:2348. - PubMed
-
- Mosmann TR, Coffman RL. TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1989;7:145. - PubMed
-
- Kaplan MH, Sun YL, Hoey T, Grusby MJ. Impaired IL-12 responses and enhanced development of Th2 cells in Stat4-deficient mice. Nature. 1996;382:174. - PubMed
-
- Meraz MA, White JM, Sheehan KC, et al. Targeted disruption of the Stat1 gene in mice reveals unexpected physiologic specificity in the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. Cell. 1996;84:431. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

