NMDA receptor activation by spontaneous glutamatergic neurotransmission
- PMID: 19261712
- PMCID: PMC2681428
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.90754.2008
NMDA receptor activation by spontaneous glutamatergic neurotransmission
Abstract
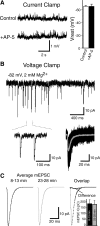
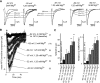
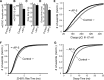
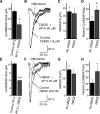
Under physiological conditions N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor activation requires coincidence of presynaptic glutamate release and postsynaptic depolarization due to the voltage-dependent block of these receptors by extracellular Mg(2+). Therefore spontaneous neurotransmission in the absence of action potential firing is not expected to lead to significant NMDA receptor activation. Here we tested this assumption in layer IV neurons in neocortex at their resting membrane potential (approximately -67 mV). In long-duration stable recordings, we averaged a large number of miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents (mEPSCs, >100) before or after application of dl-2 amino 5-phosphonovaleric acid, a specific blocker of NMDA receptors. The difference between the two mEPSC waveforms showed that the NMDA current component comprises approximately 20% of the charge transfer during an average mEPSC detected at rest. Importantly, the contribution of the NMDA component was markedly enhanced at membrane potentials expected for the depolarized up states (approximately -50 mV) that cortical neurons show during slow oscillations in vivo. In addition, partial block of the alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid (AMPA) receptor component of the mEPSCs did not cause a significant reduction in the NMDA component, indicating that potential AMPA receptor-driven local depolarizations did not drive NMDA receptor activity at rest. Collectively these results indicate that NMDA receptors significantly contribute to signaling at rest in the absence of dendritic depolarizations or concomitant AMPA receptor activity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Presynaptic and postsynaptic NMDA receptors mediate distinct effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on synaptic transmission.J Neurophysiol. 2008 Dec;100(6):3175-84. doi: 10.1152/jn.90880.2008. Epub 2008 Oct 15. J Neurophysiol. 2008. PMID: 18922945 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous NMDA-receptor activation regulates glutamate release in cultured spinal neurons.J Neurophysiol. 1998 Jul;80(1):196-208. doi: 10.1152/jn.1998.80.1.196. J Neurophysiol. 1998. PMID: 9658041
-
Presynaptic NR2B-containing NMDA autoreceptors mediate gluta-matergic synaptic transmission in the rat visual cortex.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2009 May;6(2):104-9. doi: 10.2174/156720209788185632. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2009. PMID: 19442159
-
Interaction of dopamine D1 and NMDA receptors mediates acute clozapine potentiation of glutamate EPSPs in rat prefrontal cortex.J Neurophysiol. 2002 May;87(5):2324-36. doi: 10.1152/jn.2002.87.5.2324. J Neurophysiol. 2002. PMID: 11976371
-
Contribution of AMPA and NMDA receptors to excitatory responses in the inferior colliculus.Hear Res. 2002 Jun;168(1-2):35-42. doi: 10.1016/s0378-5955(02)00372-6. Hear Res. 2002. PMID: 12117507 Review.
Cited by
-
Axonal ER Ca2+ Release Selectively Enhances Activity-Independent Glutamate Release in a Huntington Disease Model.J Neurosci. 2023 May 17;43(20):3743-3763. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1593-22.2023. Epub 2023 Mar 21. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36944490 Free PMC article.
-
Asynchronous release sites align with NMDA receptors in mouse hippocampal synapses.Nat Commun. 2021 Jan 29;12(1):677. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21004-x. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33514725 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic cooperativity regulates persistent network activity in neocortex.J Neurosci. 2013 Feb 13;33(7):3151-63. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4424-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23407969 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic basis of rapid antidepressant action.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2024 Sep 29. doi: 10.1007/s00406-024-01898-6. Online ahead of print. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39343821 Review.
-
A novel role for {gamma}-secretase: selective regulation of spontaneous neurotransmitter release from hippocampal neurons.J Neurosci. 2011 Jan 19;31(3):899-906. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4625-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21248114 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agmon A, Connors BW. Thalamocortical responses of mouse somatosensory (barrel) cortex in vitro. Neuroscience 41: 365–379, 1991. - PubMed
-
- Bekkers JM, Stevens CF. NMDA and non-NMDA receptors are co-localized at individual excitatory synapses in cultured rat hippocampus. Nature 341: 230–233, 1989. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

