Childhood obesity: are genetic differences involved?
- PMID: 19261728
- PMCID: PMC2677002
- DOI: 10.3945/ajcn.2009.27113C
Childhood obesity: are genetic differences involved?
Abstract
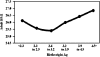
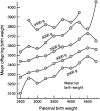
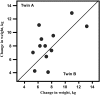
This brief review focuses on the genetic contribution to childhood obesity. Evidence for a genetic component to excess body weight during growth is presented from the perspective of genetic epidemiology studies. Parental obesity is a predictor of childhood excess weight. The familial risk ratio for childhood obesity when a parent is obese reaches >2.5. Birth weight is characterized by a genetic heritability component on the order of 30%, with significant maternal and paternal effects in addition to the newborn genes. About 5% of childhood obesity cases are caused by a defect that impairs function in a gene, and >/=5 of these genes have been uncovered. However, the common forms of childhood obesity seem to result from a predisposition that primarily favors obesogenic behaviors in an obesogenic environment. Candidate gene and genomewide association studies reveal that these obesogenic genes have small effect sizes but that the risk alleles for obesity are quite common in populations. The latter may translate into a highly significant population-attributable risk of obesity. Gene-environment interaction studies suggest that the effects of predisposing genes can be enhanced or diminished by exposure to relevant behaviors. It is possible that the prevalence of childhood obesity is increasing across generations as a result of positive assortative mating with obese husbands and wives contributing more obese offspring than normal-weight parents.
Figures
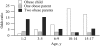

Similar articles
-
[Genetics of obesity].Vnitr Lek. 2010 Oct;56(10):1035-42. Vnitr Lek. 2010. PMID: 21105448 Review. Czech.
-
Stronger influence of maternal than paternal obesity on infant and early childhood body mass index: the Fels Longitudinal Study.Pediatr Obes. 2013 Jun;8(3):159-69. doi: 10.1111/j.2047-6310.2012.00100.x. Epub 2012 Oct 8. Pediatr Obes. 2013. PMID: 23042783 Free PMC article.
-
The influential role of genes in obesity.S D Med. 2011;Spec No:12-5, 17. S D Med. 2011. PMID: 21717811
-
Epidemic obesity: are genetic factors involved via increased rates of assortative mating?Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2000 Mar;24(3):345-53. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0801135. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2000. PMID: 10757629
-
Clinical, molecular genetics and therapeutic aspects of syndromic obesity.Clin Genet. 2019 Jan;95(1):23-40. doi: 10.1111/cge.13367. Epub 2018 May 21. Clin Genet. 2019. PMID: 29700824 Review.
Cited by
-
Associations of PON1 and genetic ancestry with obesity in early childhood.PLoS One. 2013 May 3;8(5):e62565. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062565. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23658746 Free PMC article.
-
The FTO genetic variants are associated with dietary intake and body mass index amongst Emirati population.PLoS One. 2019 Oct 17;14(10):e0223808. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223808. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31622411 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge and attitudes towards obesity among primary school children in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania.Niger Med J. 2015 Mar-Apr;56(2):103-8. doi: 10.4103/0300-1652.150692. Niger Med J. 2015. PMID: 25838624 Free PMC article.
-
The genetics of childhood obesity and interaction with dietary macronutrients.Genes Nutr. 2013 May;8(3):271-87. doi: 10.1007/s12263-013-0339-5. Epub 2013 Mar 8. Genes Nutr. 2013. PMID: 23471855 Free PMC article.
-
Early origins of child obesity: bridging disciplines and phases of development -- September 30--October 1, 2010.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2012 Apr 16;9(4):1227-62. doi: 10.3390/ijerph9041227. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2012. PMID: 23443002 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lobstein T, Baur L, Uauy R, IASO International Obesity Taskforce. Obesity in children and young people: a crisis in public health. Obes Rev 2004;5(suppl 1):4–104 - PubMed
-
- International Obesity Taskforce Childhood obesity. Available from: http://www.iotf.org/childhoodobesity.asp (cited 20 Aug 2008)
-
- World Health Organization Global strategy on diet, physical activity and health. Available from: http://www.who.int/dietphysicalactivity/childhood_what/en/index.html (cited 20 Aug 2008)
-
- Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LR, McDowell MA, Tabak CJ, Flegal KM. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in the United States, 1999–2004. JAMA 2006;295:1549–55 - PubMed
-
- Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Flegal KM. High body mass index for age among US children and adolescents, 2003–2006. JAMA 2008;299:2401–5 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

