Synaptically released zinc triggers metabotropic signaling via a zinc-sensing receptor in the hippocampus
- PMID: 19261885
- PMCID: PMC3175799
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5093-08.2009
Synaptically released zinc triggers metabotropic signaling via a zinc-sensing receptor in the hippocampus
Abstract
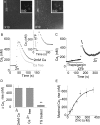
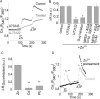
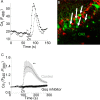
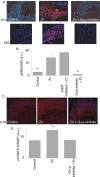
Zn(2+) is coreleased with glutamate from mossy fiber terminals and can influence synaptic function. Here, we demonstrate that synaptically released Zn(2+) activates a selective postsynaptic Zn(2+)-sensing receptor (ZnR) in the CA3 region of the hippocampus. ZnR activation induced intracellular release of Ca(2+), as well as phosphorylation of extracellular-regulated kinase and Ca(2+)/calmodulin kinase II. Blockade of synaptic transmission by tetrodotoxin or CdCl inhibited the ZnR-mediated Ca(2+) rises. The responses mediated by ZnR were largely attenuated by the extracellular Zn(2+) chelator, CaEDTA, and in slices from mice lacking vesicular Zn(2+), suggesting that synaptically released Zn(2+) triggers the metabotropic activity. Knockdown of the expression of the orphan G-protein-coupled receptor 39 (GPR39) attenuated ZnR activity in a neuronal cell line. Importantly, we observed widespread GPR39 labeling in CA3 neurons, suggesting a role for this receptor in mediating ZnR signaling in the hippocampus. Our results describe a unique role for synaptic Zn(2+) acting as the physiological ligand of a metabotropic receptor and provide a novel pathway by which synaptic Zn(2+) can regulate neuronal function.
Figures


References
-
- Aizenman E, Stout AK, Hartnett KA, Dineley KE, McLaughlin B, Reynolds IJ. Induction of neuronal apoptosis by thiol oxidation: putative role of intracellular zinc release. J Neurochem. 2000;75:1878–1888. - PubMed
-
- An WL, Pei JJ, Nishimura T, Winblad B, Cowburn RF. Zinc-induced anti-apoptotic effects in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells via the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2005;135:40–47. - PubMed
-
- Azriel-Tamir H, Sharir H, Schwartz B, Hershfinkel M. Extracellular zinc triggers ERK-dependent activation of Na+/H+ exchange in colonocytes mediated by the zinc-sensing receptor. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:51804–51816. - PubMed
-
- Berkeley JL, Levey AI. Cell-specific extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation by multiple G protein-coupled receptor families in hippocampus. Mol Pharmacol. 2003;63:128–135. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
