Germline-encoded amino acids in the alphabeta T-cell receptor control thymic selection
- PMID: 19262510
- PMCID: PMC2679808
- DOI: 10.1038/nature07812
Germline-encoded amino acids in the alphabeta T-cell receptor control thymic selection
Abstract
An alphabeta T-cell response depends on the recognition of antigen plus major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins by its antigen receptor (TCR). The ability of peripheral alphabeta T cells to recognize MHC is at least partly determined by MHC-dependent thymic selection, by which an immature T cell survives only if its TCR can recognize self MHC. This process may allow MHC-reactive TCRs to be selected from a repertoire with completely random and unbiased specificities. However, analysis of thymocytes before positive selection indicated that TCR proteins might have a predetermined ability to bind MHC. Here we show that specific germline-encoded amino acids in the TCR promote 'generic' MHC recognition and control thymic selection. In mice expressing single, rearranged TCR beta-chains, individual mutation of amino acids in the complementarity-determining region (CDR) 2beta to Ala reduced development of the entire TCR repertoire. Altogether, these results show that thymic selection is controlled by germline-encoded MHC contact points in the alphabeta TCR and indicate that the diversity of the peripheral T-cell repertoire is enhanced by this 'built-in' specificity.
Figures

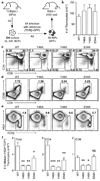
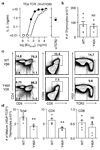

References
-
- Zinkernagel RM, Doherty PC. Restriction of in vitro T cell-mediated cytotoxicity in lymphocytic choriomeningitis within a syngeneic or semiallogeneic system. Nature. 1974;248:701–702. - PubMed
-
- Bevan MJ. In a radiation chimaera, host H-2 antigens determine immune responsiveness of donor cytotoxic cells. Nature. 1977;269:417–418. - PubMed
-
- Kisielow P, Teh HS, Bluthmann H, von Boehmer H. Positive selection of antigen-specific T cells in thymus by restricting MHC molecules. Nature. 1988;335:730–733. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI057485/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI22295/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI18785/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007405/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA046934/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI018785/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R56 AI017134/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI076463/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI07405/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI018785/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI022295/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI018785/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI057485/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

