TET2 mutations and their clinical correlates in polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia and myelofibrosis
- PMID: 19262601
- PMCID: PMC4654629
- DOI: 10.1038/leu.2009.47
TET2 mutations and their clinical correlates in polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia and myelofibrosis
Abstract
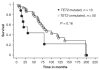
High-throughput DNA sequence analysis was used to screen for TET2 mutations in bone marrow-derived DNA from 239 patients with BCR-ABL-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs). Thirty-two mutations (19 frameshift, 10 nonsense, 3 missense; mostly involving exons 4 and 12) were identified for an overall mutational frequency of approximately 13%. Specific diagnoses included polycythemia vera (PV; n=89), essential thrombocythemia (ET; n=57), primary myelofibrosis (PMF; n=60), post-PV MF (n=14), post-ET MF (n=7) and blast phase PV/ET/MF (n=12); the corresponding mutational frequencies were approximately 16, 5, 17, 14, 14 and 17% (P=0.50). Mutant TET2 was detected in approximately 17 and approximately 7% of JAK2V617F-positive and -negative cases, respectively (P=0.04). However, this apparent clustering of the two mutations was accounted for by an independent association between mutant TET2 and advanced age; mutational frequency was approximately 23% in patients > or =60 years old versus approximately 4% in younger patients (P<0.0001). The presence of mutant TET2 did not affect survival, leukemic transformation or thrombosis in either PV or PMF; a correlation with hemoglobin <10 g per 100 ml in PMF was noted (P=0.05). We conclude that TET2 mutations occur in both JAK2V617F-positive and -negative MPN, are more prevalent in older patients, display similar frequencies across MPN subcategories and disease stages, and hold limited prognostic relevance.
Figures
References
-
- Levine RL, Wadleigh M, Cools J, Ebert BL, Wernig G, Huntly BJ, et al. Activating mutation in the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, and myeloid metaplasia with myelofibrosis. Cancer Cell. 2005;7:387–397. - PubMed
-
- James C, Ugo V, Le Couedic JP, Staerk J, Delhommeau F, Lacout C, et al. A unique clonal JAK2 mutation leading to constitutive signalling causes polycythaemia vera. Nature. 2005;434:1144–1148. - PubMed
-
- Kralovics R, Passamonti F, Buser AS, Teo SS, Tiedt R, Passweg JR, et al. A gain-of-function mutation of JAK2 in myeloproliferative disorders. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1779–1790. - PubMed
-
- Baxter EJ, Scott LM, Campbell PJ, East C, Fourouclas N, Swanton S, et al. Acquired mutation of the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in human myeloproliferative disorders. Lancet. 2005;365:1054–1061. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous