Effect of ultraviolet B radiation on activator protein 1 constituent proteins and modulation by dietary energy restriction in SKH-1 mouse skin
- PMID: 19263438
- PMCID: PMC2736326
- DOI: 10.1002/mc.20529
Effect of ultraviolet B radiation on activator protein 1 constituent proteins and modulation by dietary energy restriction in SKH-1 mouse skin
Abstract
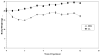
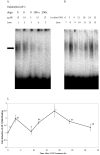
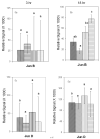
The study examined the timing of modulation of activator protein 1(AP-1):DNA binding and production of AP-1 constituent proteins by ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation and effect of dietary energy restriction [DER, 40% calorie reduction from fat and carbohydrate compared to control ad libitum (AL) diet] in SKH-1 mouse epidermis. AP-1:DNA binding by electromobility shift assay (EMSA) was increased in a biphasic manner after treatment with a tumor-promoting suberythemal dose (750 mJ/cm(2)) of UVB light (311-313 nm) with peaks at 3 and 18 h postirradiation. DER overall reduced AP-1:DNA binding in mock-treated and UVB-treated skin at 3 and 18 h after UVB treatment. The timing of modulation of production of AP-1 constituent proteins by Western blot analysis was examined at 0 h (mock treatment), 3, 9, 18, and 24 h. We found that c-jun (9 h), jun-B (9 and 18 h), phosphorylated c-jun (3 h), and fra-1 (18 h) protein levels were increased after UVB treatment compared to mock controls. In a follow-up diet experiment, animals were placed on DER or AL diet for 10-12 wk and treated with UVB as before. DER was found to completely block the UVB-induced increase in phosphorylated c-jun protein levels and decrease in fra-2 protein levels at 18 h. In addition, DER enhanced UVB-induced increase in jun B levels and lowered basal levels of c-fos seen 18 h after UVB. These data suggest that DER may be able to assist in the prevention of UVB-induced skin carcinogenesis by modulating AP-1:DNA binding and AP-1 constituent protein levels.
Figures






References
-
- de VE, van de Poll-Franse LV, Louwman WJ, de Gruijl FR, Coebergh JW. Predictions of skin cancer incidence in the Netherlands up to 2015. Br.J.Dermatol. 2005;152:481–488. - PubMed
-
- Athas WF, Hunt WC, Key CR. Changes in nonmelanoma skin cancer incidence between 1977-1978 and 1998-1999 in Northcentral New Mexico. Cancer Epidemiol.Biomarkers Prev. 2003;12:1105–1108. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein LR, Colburn NH. AP1/jun function is differentially induced in promotion-sensitive and resistant JB6 cells. Science. 1989;244:566–569. - PubMed
-
- Przybyszewski J, Yaktine AL, Duysen E, Blackwood D, Wang W, Au A, Birt DF. Inhibition of phorbol ester-induced AP-1-DNA binding, c-Jun protein and c-jun mRNA by dietary energy restriction is reversed by adrenalectomy in SENCAR mouse epidermis. Carcinogenesis. 2001;22:1421–1427. - PubMed
-
- Domann FE, Jr., Levy JP, Finch JS, Bowden GT. Constitutive AP-1 DNA binding and transactivating ability of malignant but not benign mouse epidermal cells. Mol.Carcinog. 1994;9:61–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

