Model-based automatic detection of the anterior and posterior commissures on MRI scans
- PMID: 19264138
- PMCID: PMC2674131
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.02.030
Model-based automatic detection of the anterior and posterior commissures on MRI scans
Abstract
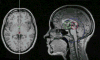
The projections of the anterior and posterior commissures (AC/PC) on the mid-sagittal plane of the human brain are important landmarks in neuroimaging. They can be used, for example, during MRI scanning for acquiring the imaging sections in a standard orientation. In post-acquisition image processing, these landmarks serve to establish an anatomically-based frame of reference within the brain that can be extremely useful in designing automated image analysis algorithms such as image segmentation and registration methods. This paper presents a fully automatic model-based algorithm for AC/PC detection on MRI scans. The algorithm utilizes information from a number of model images on which the locations of the AC/PC and a reference point (the vertex of the superior pontine sulcus) are known. This information is then used to locate the landmarks on test scans by template matching. The algorithm is designed to be fast, robust, and accurate. The method is flexible in that it can be trained to work on different image contrasts, optimized for different populations, or scanning modes. To assess the effectiveness of this technique, we compared automatically and manually detected landmark locations on 84 T(1)-weighted and 42 T(2)-weighted test scans. Overall, the average Euclidean distance between automatically and manually detected landmarks was 1.1 mm. A software implementation of the algorithm is freely available online at www.nitrc.org/projects/art.
Figures

References
-
- Ardekani BA, Choi SJ, Hossein-Zadeh GA, Porjesz B, Tanabe JL, Lim KO, Bilder R, Helpern JA, Begleiter H. Functional magnetic resonance imaging of brain activity in the visual oddball task. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res. 2002;14:347–356. - PubMed
-
- Ardekani BA, Kershaw J, Braun M, Kanno I. Automatic detection of the mid-sagittal plane in 3-D brain images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 1997;16:947–952. - PubMed
-
- Boesen K, Frey S, Huang J, Germann J, Stern J, Collins DL, Evans AC, Rottenberg DA. Inter-rater reproducibility of 3D cortical and sub-cortical landmark points. 11th Annual Meeting of the Organization for Human Brain Mapping; Toronto, Canada. 2005.
-
- Han Y, Park H. Automatic registration of brain magnetic resonance images based on Talairach reference system. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2004;20:572–580. - PubMed
-
- Hu Q, Nowinski WL. A rapid algorithm for robust and automatic extraction of the midsagittal plane of the human cerebrum from neuroimages based on local symmetry and outlier removal. Neuroimage. 2003;20:2153–2165. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

