Phenomenology, longitudinal course, and outcome of children and adolescents with bipolar spectrum disorders
- PMID: 19264264
- PMCID: PMC2713171
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chc.2008.11.002
Phenomenology, longitudinal course, and outcome of children and adolescents with bipolar spectrum disorders
Abstract
Pediatric bipolar disorder (BPD) significantly affects the normal emotional, cognitive, and social development. The course of children and adolescents with BPD is manifested by frequent changes in symptoms polarity showing a dimensional continuum of bipolar symptoms severity from subsyndromal to mood syndromes meeting full DSM-IV criteria. Thus, early diagnosis and treatment of pediatric bipolar is of utmost importance.
Figures
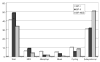
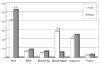
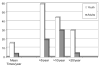
References
-
- Kowatch RA, Youngstrom EA, Danielyan A, et al. Review and meta-analysis of the phenomenology and clinical characteristics of mania in children and adolescents. Bipolar Disord. 2005;7:483–496. - PubMed
-
- Pavuluri MN, Birmaher B, Naylor M. Pediatric bipolar disorder: A review of the past 10 years. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2005;44(9):846–71. - PubMed
-
- Axelson D, Birmaher B, Strober M, et al. Phenomenlogy of children and adolescents with bipolar spectrum disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006;63(10):1139–48. - PubMed
-
- Soutullo CA, Chang KD, Diez-Suarez A, et al. Bipolar disorder in children and adolescents: international perspective on epidemiology and phenomenology. Bipolar Disord. 2005;7(6):497–506. - PubMed
-
- McClellan J, Kowatch Ra, Findling RL. Practice parameter for the assessment and treatment of children and adolescents with bipolar disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2007;46(1):107–25. - PubMed

