A truncated T antigen expressed from an alternatively spliced BK virus early mRNA
- PMID: 19264611
- PMCID: PMC2887564
- DOI: 10.1099/vir.0.009159-0
A truncated T antigen expressed from an alternatively spliced BK virus early mRNA
Abstract
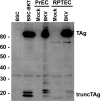
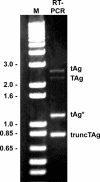
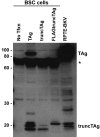
The early region of BK virus (BKV) is known to encode two well-characterized tumour (T) antigens, large T antigen (TAg) and small T antigen (tAg). In this study, we provide evidence of a third early BKV mRNA that codes for an additional early region product with an apparent molecular mass of 17-20 kDa. This truncated form of TAg (truncTAg) is expressed from an alternatively spliced mRNA that is derived from the excision of a second intron from the mRNA encoding TAg. The first 133 aa of truncTAg are identical to those of TAg but the additional splice results in translation from a different reading frame, adding three new amino acids before reaching a stop codon. TruncTAg is expressed in both BKV-transformed and lytically infected cells and it is found to be primarily localized to the nucleus. The function of BKV truncTAg is likely to be relevant to transformation, similar to the additional T antigens of simian virus 40, JC virus and mouse polyomavirus.
Figures
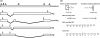
References
-
- Ahuja, D., Sáenz-Robles, M. T. & Pipas, J. M. (2005). SV40 large T antigen targets multiple cellular pathways to elicit cellular transformation. Oncogene 24, 7729–7745. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

