The Epstein-Barr virus alkaline exonuclease BGLF5 serves pleiotropic functions in virus replication
- PMID: 19264771
- PMCID: PMC2682060
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00170-09
The Epstein-Barr virus alkaline exonuclease BGLF5 serves pleiotropic functions in virus replication
Abstract
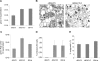
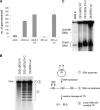
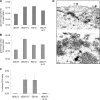
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) alkaline exonuclease BGLF5 has previously been recognized to contribute to immune evasion by downregulating production of HLA molecules during virus replication. We have constructed a BGLF5-null virus mutant to determine BGLF5's functions during EBV viral replication. Quantification of virus production in permissive 293 cells carrying a DeltaBGLF5 genome identified a 17- to 21-fold reduction relative to complemented or wild-type controls. Detailed monitoring of DeltaBGLF5 replication evidenced an impaired virus nucleocapsid maturation, a reduced primary egress and a 1.4-fold reduction in total viral DNA synthesis. DeltaBGLF5 single-unit-length viral genomes were not only less abundant but also migrated faster than expected in gel electrophoresis. We concluded that BGLF5 pertained both to the generation and to the processing of viral linear genomes. DeltaBGLF5 phenotypic traits were reminiscent of those previously identified in a mutant devoid of UL12, BGLF5's homolog in herpes simplex virus type 1, and indeed UL12 was found to partially complement the DeltaBGLF5 phenotype. However, BGLF5-specific functions could also be identified; the nuclear membrane of replicating cells displayed images of reduplication and complex folding that could be completely corrected by BGLF5 but not UL12. Similar nuclear abnormalities were previously observed in cells transfected with BFLF2 and BFRF1, two viral proteins crucial for EBV nuclear egress. Interestingly, DeltaBGLF5 cells produced more BFLF2 than wild-type or complemented counterparts. The present study provides an overview of BGLF5's functions that will guide future molecular studies. We anticipate that the 293/DeltaBGLF5 cell line will be instrumental in such developments.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The Epstein-Barr virus protein kinase BGLF4 and the exonuclease BGLF5 have opposite effects on the regulation of viral protein production.J Virol. 2009 Nov;83(21):10877-91. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00525-09. Epub 2009 Aug 26. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19710145 Free PMC article.
-
The "Bridge" in the Epstein-Barr virus alkaline exonuclease protein BGLF5 contributes to shutoff activity during productive infection.J Virol. 2012 Sep;86(17):9175-87. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00309-12. Epub 2012 Jun 13. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22696660 Free PMC article.
-
BFRF1 of Epstein-Barr virus is essential for efficient primary viral envelopment and egress.J Virol. 2005 Mar;79(6):3703-12. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.6.3703-3712.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15731264 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus evasion of CD8(+) and CD4(+) T cell immunity via concerted actions of multiple gene products.Semin Cancer Biol. 2008 Dec;18(6):397-408. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2008.10.008. Epub 2008 Oct 25. Semin Cancer Biol. 2008. PMID: 18977445 Review.
-
Contribution of viral recombinants to the study of the immune response against the Epstein-Barr virus.Semin Cancer Biol. 2008 Dec;18(6):409-15. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2008.09.001. Epub 2008 Sep 30. Semin Cancer Biol. 2008. PMID: 18938248 Review.
Cited by
-
DNA processing by the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus alkaline exonuclease SOX contributes to viral gene expression and infectious virion production.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jan 11;51(1):182-197. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1190. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36537232 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of activation of the BNLF2a immune evasion gene of Epstein-Barr virus by Zta.J Gen Virol. 2018 Jun;99(6):805-817. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.001056. Epub 2018 Mar 26. J Gen Virol. 2018. PMID: 29580369 Free PMC article.
-
Host shutoff is a conserved phenotype of gammaherpesvirus infection and is orchestrated exclusively from the cytoplasm.J Virol. 2009 Sep;83(18):9554-66. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01051-09. Epub 2009 Jul 8. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19587049 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Implications of Epstein-Barr Virus Lytic Genes in Carcinogenesis.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 24;14(23):5780. doi: 10.3390/cancers14235780. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36497262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epstein-Barr virus DNase (BGLF5) induces genomic instability in human epithelial cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Apr;38(6):1932-49. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp1169. Epub 2009 Dec 23. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20034954 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baer, R., A. T. Bankier, M. D. Biggin, P. L. Deininger, P. J. Farrell, T. J. Gibson, G. Hatfull, G. S. Hudson, S. C. Satchwell, C. Seguin, P. S. Tufnell, and B. G. Barell. 1984. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature 310207-211. - PubMed
-
- Chen, H. F., M. Sauter, P. Haiss, and N. Muller-Lantzsch. 1991. Immunological characterization of the Epstein-Barr virus phosphoprotein PP58 and deoxyribonuclease expressed in the baculovirus expression system. Int. J. Cancer 48879-888. - PubMed
-
- Chen, M. R., T. Y. Hsu, J. Y. Chen, and C. S. Yang. 1990. Molecular characterization of a cDNA clone encoding the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNase. J. Virol. Methods 29127-141. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

