Bacillus cereus-induced permeability of the blood-ocular barrier during experimental endophthalmitis
- PMID: 19264886
- PMCID: PMC2880527
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.08-3051
Bacillus cereus-induced permeability of the blood-ocular barrier during experimental endophthalmitis
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to determine to what extent blood-retinal barrier (BRB) permeability occurred during experimental Bacillus cereus endophthalmitis and whether tight junction alterations were involved in permeability.
Methods: Mice were intravitreally injected with 100 colony-forming units of B. cereus, and eyes were analyzed at specific times after infection for permeability to fibrin and albumin, quantitation of intraocular plasma constituent leakage, production of inflammatory cytokines, and alterations in tight junction protein localization and expression at the level of the retinal pigment epithelium.
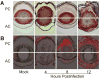
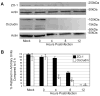
Results: B. cereus induced the leakage of albumin and fibrin into the aqueous and vitreous humor by 8 hours after infection. BRB permeability occurred as early as 4 hours and increased 13.30-fold compared with uninfected controls by 8 hours. Production of proinflammatory cytokines IL-6, MIP-1alpha, IL-1beta, and KC increased over the course of infection. In the retina, ZO-1 disruption began by 4 hours and was followed by decreasing occludin and ZO-1 expression at 4 and 8 hours, respectively. Tubulin condensation and RPE65 degradation occurred by 12 hours. A quorum-sensing mutant B. cereus strain caused BRB permeability comparable to that of wild-type B. cereus. Wild-type and mutant B. cereus sterile supernatants induced blood-ocular barrier permeability similarly to that of wild-type infection.
Conclusions: These results indicate that BRB permeability occurs during the early stages of experimental B. cereus endophthalmitis, beginning as early as 4 hours after infection. Disruption of tight junctions at the level of the retinal pigment epithelium may contribute to barrier breakdown. Quorum-sensing dependent factors may not significantly contribute to BRB permeability.
Figures






Similar articles
-
A role for tumor necrosis factor-alpha in experimental Bacillus cereus endophthalmitis pathogenesis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008 Oct;49(10):4482-9. doi: 10.1167/iovs.08-2085. Epub 2008 Jun 27. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008. PMID: 18586878 Free PMC article.
-
Bacillus cereus induces permeability of an in vitro blood-retina barrier.Infect Immun. 2008 Apr;76(4):1358-67. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01330-07. Epub 2008 Feb 11. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18268029 Free PMC article.
-
Role of swarming migration in the pathogenesis of bacillus endophthalmitis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006 Oct;47(10):4461-7. doi: 10.1167/iovs.06-0301. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006. PMID: 17003440
-
Toward improving therapeutic regimens for Bacillus endophthalmitis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008 Apr;49(4):1480-7. doi: 10.1167/iovs.07-1303. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008. PMID: 18385066 Free PMC article.
-
Remodeling of junctional complexes during the development of the outer blood-retinal barrier.Anat Rec. 1997 Nov;249(3):380-8. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0185(199711)249:3<380::AID-AR9>3.0.CO;2-Y. Anat Rec. 1997. PMID: 9372172
Cited by
-
Toll-like receptor 2 ligand pretreatment attenuates retinal microglial inflammatory response but enhances phagocytic activity toward Staphylococcus aureus.Infect Immun. 2012 Jun;80(6):2076-88. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00149-12. Epub 2012 Mar 19. Infect Immun. 2012. PMID: 22431652 Free PMC article.
-
Oral administration of S-nitroso-L-glutathione (GSNO) provides anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective effects during ocular bacterial infections.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023 Sep 28;80(10):309. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-04963-w. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37770649 Free PMC article.
-
Divergence of the SigB regulon and pathogenesis of the Bacillus cereus sensu lato group.BMC Genomics. 2012 Oct 22;13:564. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-564. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 23088190 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of CCL2 and CCL3 in intraocular inflammation during Bacillus endophthalmitis.Exp Eye Res. 2022 Nov;224:109213. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2022.109213. Epub 2022 Sep 2. Exp Eye Res. 2022. PMID: 36063964 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Staphylococcus aureus Virulence Factors in Inducing Inflammation and Vascular Permeability in a Mouse Model of Bacterial Endophthalmitis.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 8;10(6):e0128423. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128423. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26053426 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

